TS Inter 2nd Year – History Previous Paper 2022
SECTION A
Note:
- Answer ANY THREE of the following questions in 40 lines.
- Each question carries TEN marks.
1. Trace the geographical features of Telangana.
Telangana, a southern Indian state, boasts a captivating geographical landscape, contributing significantly to its unique identity and resource potential.
-
Location and Borders: Strategically positioned in the Deccan Plateau, Telangana shares borders with Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh to the north, Andhra Pradesh to the east and south, and Karnataka to the west. This location grants it access to diverse climatic influences and a rich array of natural resources.
-
Topography: The state exhibits a varied topography, ranging from rolling hills and plateaus to fertile plains. The Deccan Plateau, a prominent geological formation, dominates the landscape, characterized by its undulating terrain and black soil.
The Eastern Ghats, a mountain range, intrudes into the state, adding to its scenic beauty and contributing to regional rainfall patterns. -
Rivers: The Godavari and Krishna, two major peninsular rivers, traverse Telangana, shaping its agricultural landscape and supporting a vibrant riverine ecosystem. The Manjra, Pranhita, and Tungabhadra, tributaries of these major rivers, further enrich the state’s water resources. These rivers not only provide irrigation for agriculture but also contribute to the state’s hydroelectric power generation.
-
Climate: Telangana experiences a tropical savanna climate, characterized by hot summers and moderate winters.
The state receives rainfall primarily during the monsoon season, with variations across regions. This climatic pattern influences agricultural practices and the state’s natural vegetation. -
Natural Resources: Telangana is endowed with a wealth of natural resources. Mineral deposits, including coal, iron ore, limestone, and dolomite, are abundant, forming the bedrock of the state’s industrial development. The state also possesses significant forest cover, providing timber, non-timber forest products, and ecological services. -
2. Estimate the greatness of Kakatiya Ganapatideva.
Kakatiya Ganapatideva, who ruled from 1199 to 1261 CE, stands as a towering figure in the history of Telangana.
-
Military Prowess and Political Expansion: Ganapatideva was a formidable military leader who expanded the Kakatiya kingdom significantly.
He successfully defended his kingdom against attacks from neighboring powers, ensuring its territorial integrity and political stability. His military successes not only expanded the kingdom’s boundaries but also strengthened its position in the regional power dynamics. -
Patron of Art and Culture: Ganapatideva was a passionate patron of art and culture. He commissioned the construction of numerous temples and religious structures, including the iconic Thousand Pillar Temple in Hanamkonda. This architectural marvel stands as a testament to the artistic brilliance of the Kakatiya era. His patronage extended to Telugu literature and music, fostering a vibrant cultural milieu. -
Economic Prosperity: Ganapatideva implemented sound economic policies that led to significant economic growth. He encouraged agriculture and trade, improving irrigation infrastructure and fostering a conducive environment for economic activity. This economic prosperity not only strengthened the Kakatiya kingdom but also improved the livelihoods of its citizens. -
Administrative Reforms: Ganapatideva introduced administrative reforms to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of governance. He strengthened the revenue collection system, ensuring a steady flow of resources for the state. He also improved the judicial system, ensuring justice and maintaining law and order.
3. Describe the administrative system of Kakatiyas.
The Kakatiya dynasty, renowned for its political and military prowess, also established a well-organized and efficient administrative system that played a crucial role in its rise and consolidation.
-
Centralized Administration: At the apex of the Kakatiya administration stood the king, who exercised supreme authority. He was assisted by a council of ministers, who advised him on various matters of state policy. This council played a vital role in decision-making and ensuring effective governance.
-
Provincial Administration: The Kakatiya kingdom was divided into provinces, each governed by a provincial governor. These governors were responsible for maintaining law and order, collecting revenue, and administering justice within their respective provinces. This decentralized approach ensured efficient administration across the vast kingdom.
-
Revenue Administration: Revenue collection was a key function of the Kakatiya administration. Land revenue formed the principal source of income, with various taxes levied on agriculture, trade, and other economic activities. The administration implemented a system of efficient revenue collection, ensuring a steady flow of resources for the state.
-
Military Administration: The Kakatiyas maintained a strong military force to defend their kingdom and expand their territory.
They had a well-organized army comprising cavalry, infantry, and elephants. The military played a crucial role in maintaining law and order and ensuring the security of the kingdom. -
Judicial Administration: The Kakatiya administration established a well-developed judicial system to ensure justice and maintain law and order. Courts were established at various levels to hear cases and administer justice. This system ensured that justice was accessible to all citizens, irrespective of their social or economic status.
4. Discuss the achievements of Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah?
Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah, the fifth ruler of the Qutub Shahi dynasty, left an indelible mark on the history of Hyderabad. His reign, from 1550 to 1580 CE, witnessed a period of significant cultural and architectural development.
-
Founder of Hyderabad: Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah is credited with founding the city of Hyderabad in 1591. He meticulously planned and developed the city, giving it its distinctive architectural style. The city’s layout, with its grand avenues, spacious squares, and impressive monuments, reflects the vision and foresight of its founder.
-
Patron of Art and Culture: Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah was a great patron of art and culture.
He encouraged the development of music, literature, and architecture. His reign witnessed the flourishing of the Qutub Shahi style of architecture, exemplified by iconic structures like the Charminar and the Golconda Fort. These architectural marvels continue to stand as symbols of Hyderabad’s rich cultural heritage. -
Economic Development: Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah fostered economic development by promoting trade and commerce. He attracted merchants and artisans from across the region, contributing to the city’s economic growth. He also encouraged the development of industries like textiles and handicrafts, providing employment opportunities for the local population. -
Religious Tolerance: Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah was known for his religious tolerance and promoted harmony among different communities. He allowed people of different faiths to practice their religion freely, creating a culturally and religiously diverse society.
This policy of religious tolerance contributed to the city’s cosmopolitan character and fostered a sense of communal harmony. -
5. Enumerate the importance of Salar Jung reforms.
Salar Jung I, who served as the Nizam’s Prime Minister from 1853 to 1883, implemented a series of significant reforms that had a profound impact on the administration and development of the Hyderabad State.
-
Administrative Reforms: Salar Jung introduced several administrative reforms to improve the efficiency and accountability of the government.
He streamlined the revenue collection system, introduced new regulations to curb corruption, and strengthened the administrative apparatus. These reforms led to improved governance and enhanced public service delivery. -
Economic Development: Salar Jung implemented policies to promote economic development, such as investing in infrastructure, encouraging trade and commerce, and promoting industrial development. These policies led to economic growth and improved the livelihoods of the people -
Social Reforms: Salar Jung introduced several social reforms to improve the lives of the people. He abolished some of the oppressive taxes, introduced measures to improve education and healthcare, and promoted social welfare programs. These reforms contributed to the social and economic upliftment of the people of Hyderabad. -
Cultural Development: Salar Jung was a great patron of art and culture. He established the Salar Jung Museum, which houses a vast collection of artifacts from across the world. This museum stands as a testament to his love for art and his commitment to preserving cultural heritage. 6. Examine the main events of the Peasant Armed Struggle in Telangana.
The Telangana Peasant Armed Struggle, a significant chapter in the history of India’s freedom movement, unfolded between 1946 and 1951 in the Telangana region of Hyderabad State. It was a powerful uprising against the oppressive feudal system and the exploitation of peasants by landlords.
Key Events:
-
Rise of Feudal Oppression: The Nizam’s rule in Hyderabad State was characterized by a deeply entrenched feudal system. Landlords, known as Jagirdars, exercised absolute control over peasants, demanding exorbitant rents and subjecting them to various forms of exploitation. This led to widespread discontent and resentment among the peasantry.
-
Formation of Peasant Organizations: To address their grievances, peasants began organizing themselves into unions and associations. These organizations, influenced by communist ideology, sought to mobilize and empower the peasantry to fight for their rights.
-
Emergence of Armed Resistance: The initial protests and agitations gradually escalated into armed resistance. Peasants formed armed squads, known as “People’s Guerrillas,” to defend themselves against the oppressive rule of landlords and the police. These squads engaged in armed clashes with the landlords and their supporters.
-
Key Leadership: The struggle was led by prominent figures like Komaram Bheem, who emerged as a symbol of peasant resistance. His leadership inspired and motivated the peasantry to fight for their rights.
-
Spread of the Movement: The struggle spread rapidly across the Telangana region, gaining momentum and attracting widespread support. Peasants from different villages and communities united to fight against their common oppressors.
-
Government Crackdown: The Nizam’s government responded to the uprising with brutal force. The police and military were deployed to suppress the peasant movement, leading to widespread violence and casualties.
-
Integration with the Indian Union: The struggle gained further momentum after India’s independence in 1947. The integration of Hyderabad State into the Indian Union in 1948 provided a crucial turning point. The Indian government, recognizing the legitimacy of the peasant struggle, intervened to end the feudal system and implement land reforms.
-
Impact and Legacy: The Telangana Peasant Armed Struggle played a pivotal role in dismantling the feudal system and empowering the peasantry. It paved the way for land reforms and social justice in the region. The struggle also inspired other peasant movements across India, demonstrating the power of collective action in challenging oppression and fighting for social change.
7. Discuss the importance of Mass Protests in the Later Telangana Movement.
The later Telangana movement, which culminated in the formation of the state of Telangana in 2014, witnessed a resurgence of mass protests as a powerful tool for political mobilization and social change.
Importance of Mass Protests:
-
Mobilizing Public Opinion: Mass protests played a crucial role in mobilizing public opinion in favor of statehood. The sheer scale and intensity of the protests demonstrated the strength of the movement and put immense pressure on the political establishment.
-
Raising Awareness: The protests served as a platform to raise awareness about the historical, cultural, and economic injustices faced by the Telangana region. They highlighted the unique identity and aspirations of the people of Telangana.
-
Uniting the Movement: Mass protests united people from different backgrounds and social strata, fostering a sense of collective identity and shared purpose. They provided a common platform for students, employees, farmers, and other sections of society to express their demands for a separate state.
-
Pressurizing the Government: The sustained nature of the protests put immense pressure on the central and state governments. The government could no longer ignore the demands of the people, as the protests posed a significant challenge to political stability.
-
Shaping Public Discourse: The protests shaped public discourse on the issue of statehood. They brought the issue to the forefront of national attention, generating widespread debate and discussion.
-
Democratizing the Political Process: The protests demonstrated the power of people’s movements in influencing political decision-making. They highlighted the importance of public participation and dissent in a democratic society.
-
SECTION – B
Note:
- Answer ANY EIGHT of the following questions in 20 lines.
- Each question carries FIVE marks.
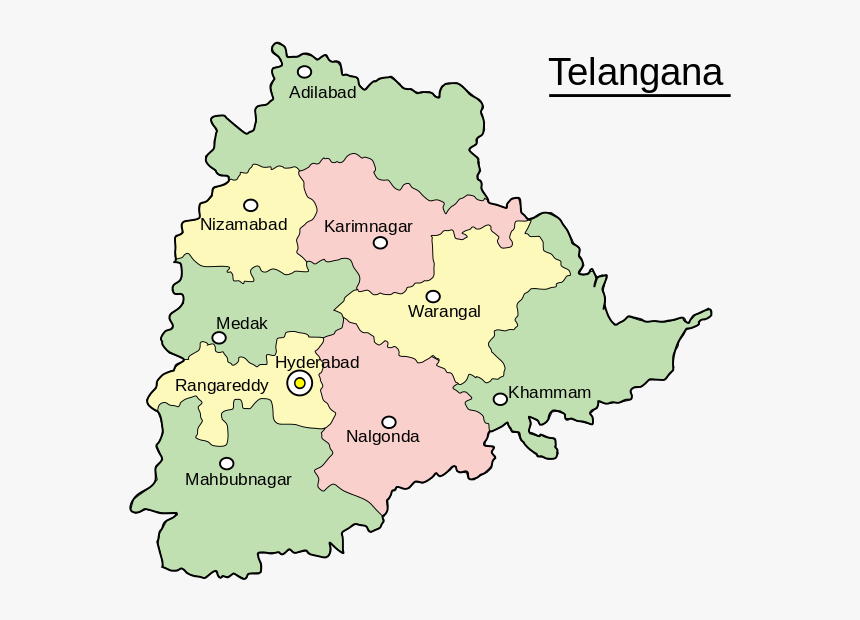
- Question No. 25 (Map pointing) is compulsory.
8. Write short notes on Rivers of Telangana.
Telangana is blessed with a network of rivers that play a vital role in its ecology, agriculture, and economy.
- Godavari: The largest river in the state, flowing through the northern part. It is a major source of irrigation and hydroelectric power.
- Krishna: Another significant river, flowing through the southern part. It also serves as a major source of irrigation and hydroelectric power.
- Manjra: A tributary of the Godavari, flowing through the central part of the state.
- Pranhita: Formed by the confluence of the Godavari and Wardha rivers, it flows through the northern part.
- Tungabhadra: A tributary of the Krishna, flowing through the southern part.
These rivers contribute to the state’s agricultural prosperity and its overall ecological balance.
9. Write about achievements of Gautamiputra Satakarni.
Gautamiputra Satakarni was a renowned ruler of the Satavahana dynasty. His reign marked a golden age for the dynasty.
- Military Victories: He defeated the Shakas and re-established Satavahana power in the Deccan.
- Expansion of Territory: He expanded the Satavahana empire significantly, bringing vast territories under his control.
- Patronage of Arts and Culture: He was a great patron of art and culture, fostering the growth of literature, music, and architecture.
- Gold Coinage: He introduced gold coinage, which stabilized the economy and promoted trade.
10. Discuss the religious conditions during the Satavahana Period.
The Satavahana period witnessed a flourishing of religious and cultural activities.
- Buddhism and Jainism: Both Buddhism and Jainism thrived during this period. Numerous Buddhist and Jain establishments, including stupas and monasteries, were built.
- Hinduism: Hinduism also continued to flourish, with various sects and schools of thought gaining prominence.
- Religious Tolerance: The Satavahana rulers were generally tolerant of different religions, fostering a climate of religious pluralism.
11. Write short notes on Vemulavada Chalukyans contribution to Telangana.
The Vemulavada Chalukyas were a local dynasty that ruled parts of Telangana during the 11th and 12th centuries.
- Architectural Contributions: They are best known for their architectural contributions. They built several temples, including the famous Ramappa Temple, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Local Rule: They provided local governance and stability to the regions they ruled.
12. Estimate the greatness of Rudradeva.
Rudradeva, also known as Rudramadeva, was a powerful ruler of the Kakatiya dynasty.
- Military Prowess: She was a skilled warrior and a successful military leader. She expanded the Kakatiya kingdom and defended it against various threats.
- Effective Administration: She was a capable administrator who maintained law and order and ensured the welfare of her subjects.
- Patronage of Arts and Culture: She was a patron of art and culture, supporting the development of Telugu literature and music.
13. Discuss the greatness of Rudramadevi.
Rudramadevi, also known as Rudradeva, was a remarkable ruler of the Kakatiya dynasty.
- First Woman Ruler: She is considered to be one of the first independent women rulers in Indian history.
- Military Victories: She was a skilled warrior and a successful military leader. She led her armies into battle and achieved significant victories against her enemies.
- Effective Governance: She was a capable administrator who maintained law and order and ensured the welfare of her subjects.
- Patronage of Arts and Culture: She was a patron of art and culture, supporting the development of Telugu literature and music.
SECTION – C
Note:
- Answer ANY FIFTEEN of the following questions in 5 lines.
- Each question carries TWO marks.
26. Write about Telanganaku Haritaharam.
Telanganaku Haritaharam is a massive tree planting drive initiated by the Telangana government. It aims to increase green cover, improve air quality, and mitigate climate change.
27. Mention about Naneghat Inscription.
The Naneghat Inscription is an important epigraphic record from the Satavahana period. It provides valuable information about the reign of Gautamiputra Satakarni.
28. Write about Hala.
Hala was a renowned Telugu poet who flourished during the Satavahana period. He is best known for his work “Ghatothkachavadham,” an epic poem in the Telugu language.
29. Write about Vishnukundins contribution to Telangana.
The Vishnukundins were a powerful dynasty that ruled parts of Telangana during the 5th and 6th centuries CE. They contributed to the region’s cultural and architectural development.
30. Write about Mudigonda Chalukyas.
The Mudigonda Chalukyas were a local dynasty that ruled parts of Telangana during the 11th and 12th centuries. They are known for their architectural contributions, including the construction of several temples.
31. Write about Chandupatla Inscription.
The Chandupatla Inscription is an important epigraphic record that provides valuable information about the history and administration of the Kakatiya dynasty.
32. Write about Nayankara System.
The Nayankara System was a decentralized system of administration prevalent in Vijayanagara and other South Indian kingdoms. It involved granting land revenue rights to local chieftains (Nayakars) in return for military service.
33. Write about Golconda.
Golconda is a historic fort and citadel situated in Hyderabad, Telangana. It was the capital of the Qutub Shahi dynasty and is known for its impressive architecture and rich history.
34. Write about Char Minar.
Char Minar is an iconic landmark in Hyderabad, Telangana. It is a monument with four minarets and is considered to be a symbol of the city. It was built during the reign of Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah.
35. Write about Urs Festivals.
Urs Festivals are religious festivals celebrated to commemorate the death anniversaries of Sufi saints and other religious figures. They are an important part of the cultural and religious landscape of Telangana.
36. Write about Ceded Districts.
The Ceded Districts refer to a group of districts in southern Telangana that were ceded to the British by the Nizam of Hyderabad in 1801. These districts played a significant role in the history and development of the region.
37. Write about Cession of Berar.
The Cession of Berar refers to the transfer of the Berar region from the Nizam’s rule to British control in 1902. This event had a significant impact on the political and economic landscape of the region.
38. Write about Osmania University.
Osmania University is a public university located in Hyderabad, Telangana. It was established in 1918 and is one of the oldest and most prestigious universities in India.
39. Write about Suravaram Pratap Reddy.
Suravaram Pratap Reddy was a renowned Telugu writer and social reformer. He was a prominent figure in the Telangana movement and played a crucial role in promoting Telugu language and literature.
40. Write about Chanda Railway Scheme.
The Chanda Railway Scheme was a controversial railway project proposed during the Nizam’s rule. It aimed to connect Hyderabad to the port of Chanda in Maharashtra. However, the project faced opposition and was never fully implemented.
41. Write about Arege Rama Swamy.
Arege Rama Swamy was a prominent social reformer and political activist in Telangana. He played a key role in the Telangana movement and fought for the rights of the peasantry.
42. Write about Vetti System.
The Vetti System was a form of forced labor prevalent in some parts of Telangana during the pre-independence era. It involved the exploitation of the labor of certain communities for the benefit of landlords or other powerful individuals.
43. Write about Chityala Ailamma.
Chityala Ailamma was a legendary woman warrior from Telangana. She is revered for her courage and bravery in fighting against injustice and oppression.
44. Write about Turrebhaj Khan.
Turrebhaj Khan was a renowned Urdu poet and scholar from Hyderabad. He is considered one of the pioneers of modern Urdu poetry in the Deccan region.
45. Write about Padmaja Naidu.
Padmaja Naidu was a prominent Indian politician and social activist. She served as the Governor of West Bengal and Orissa. She was also a noted sportsperson and represented India in tennis at the international level.
46. Write about Aghoranath Chattopadhyaya.
Aghoranath Chattopadhyaya was a renowned Bengali writer and scholar. He was a prominent figure in the Bengali Renaissance and made significant contributions to Bengali literature and culture.
47. Write about 1952 Mulki Movement.
The 1952 Mulki Movement was a protest movement in Hyderabad State against the Mulki Rules, which gave preference to local residents in government jobs. The movement was led by non-local employees who felt discriminated against.
48. Write about Marri Chenna Reddy.
Marri Chenna Reddy was a prominent Indian politician who served as the Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh. He played a significant role in the development of the state and was known for his contributions to education and social welfare.
49. Write about TJAC.
TJAC stands for Telangana Joint Action Committee. It was a broad-based coalition of various organizations and individuals that spearheaded the movement for the creation of a separate Telangana state.
50. Write about the Role of Students in Telangana Movement.
Students played a crucial role in the Telangana movement. They actively participated in protests, demonstrations, and other forms of agitation, demanding the creation of a separate state for Telangana. Their energy and enthusiasm were instrumental in mobilizing public opinion and putting pressure on the government.
