2024 – Physical Sciences
SECTION – I
Each question carries 2 marks
1. Write any two daily life uses of Baking Soda.
- As a Cleaning Agent: Baking soda can be used to clean various surfaces, including countertops, sinks, and ovens. It helps to remove stains and odors due to its mild abrasiveness and odor-neutralizing properties.
- As a Deodorizer: Baking soda is commonly used in refrigerators, carpets, and shoes to neutralize odors. It absorbs and neutralizes unpleasant smells rather than masking them.
2. Write the required materials, chemicals for the “esterification reaction” activity.
Materials:
- A beaker or flask
- A heating source (like a Bunsen burner or hot plate)
- A condenser (if necessary for distillation)
Chemicals:
- Carboxylic Acid (e.g., Acetic acid)
- Alcohol (e.g., Ethanol)
- Concentrated Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Used as a catalyst for the reaction.
3. Guess and write, what changes may happen to the focal length and position of the optic centre of a Convex lens, if it is broken into two pieces?
When a convex lens is broken into two pieces:
- Focal Length: The focal length of each piece would change. A convex lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, and breaking it would alter its curvature. This would likely result in shorter focal lengths for each piece compared to the original lens.
- Position of the Optic Centre: The optic centre of each broken piece would shift. The optic centre of a convex lens is typically in the middle, but when it is broken, the optic centre of each piece would be closer to the centre of the respective smaller lens. Each piece will now act as a smaller lens with its own optical properties.
SECTION – II
Each question carries 4 marks
4. Mention the four physical methods of concentration of the ore and explain any two of them.
Four Physical Methods of Concentration of Ore:
- Handpicking
- Froth Flotation
- Magnetic Separation
- Leaching
Explanation of Two Methods:
- Handpicking: This method is used when the ore is found in large chunks along with impurities. The process involves manually picking out the desired ore from the waste material. It is a simple method commonly used for ores that have large and visible particles, like in the case of gold and diamonds.
- Froth Flotation: This method is used to separate ores from their impurities based on the differences in their wetting properties. The ore is mixed with water and a frothing agent, and air is passed through the mixture. The hydrophobic ore particles attach to the bubbles and float to the surface, where they can be skimmed off. This method is commonly used for sulfide ores, such as those of copper and lead.
5. Write any four applications of Faraday’s “Electromagnetic Induction”, and explain any two of them.
Applications of Faraday’s Electromagnetic Induction:
- Electric Generators
- Transformers
- Induction Cooktops
- Electric Motors
Explanation of Two Applications:
- Electric Generators: Faraday’s law is fundamental in the working of electric generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. When a conductor (such as a copper coil) moves through a magnetic field, an electric current is induced in the conductor. This is the principle behind most power generation plants, where turbines rotate to induce current in generators.
- Transformers: Transformers work based on electromagnetic induction. A transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around a magnetic core. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a current in the secondary coil. This allows the transformer to step up or step down voltage for power transmission and distribution.
6. Observe the information given in the table. Answer the questions given below.
| Element | Electronic Configuration |
|---|---|
| Be | 1s² 2s² |
| Mg | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² |
| P | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p³ |
| Ne | 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ |
(i) Which of the given are s-block elements?
The s-block elements are those whose outermost electrons are in the s-orbital.
- Be (Beryllium) has the electronic configuration 1s² 2s² (outermost electrons in 2s orbital), so it is an s-block element.
- Mg (Magnesium) has the electronic configuration 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² (outermost electrons in 3s orbital), so it is an s-block element.
Thus, Be and Mg are s-block elements.
(ii) Which of the given has least valency?
Valency is determined by the number of electrons in the outer shell that an element can lose, gain, or share to form a bond.
- Be (Beryllium) has 2 valence electrons in its 2s orbital, so its valency is 2.
- Mg (Magnesium) has 2 valence electrons in its 3s orbital, so its valency is 2.
- P (Phosphorus) has 5 valence electrons in its 3p orbital, so its valency is typically 3 or 5.
- Ne (Neon) has 8 valence electrons and is chemically inert, meaning its valency is 0.
Thus, Ne has the least valency (valency = 0).
(iii) Which of the given is the 15th Group element?
The 15th group of the periodic table consists of elements that have 5 valence electrons.
- P (Phosphorus) has the electronic configuration 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p³, indicating 5 valence electrons, which places it in Group 15.
Thus, P (Phosphorus) is the 15th Group element.
(iv) Which of the given are of the same Period?
The period of an element is determined by the highest energy level (shell) in which the electrons are present.
- Be has its outermost electrons in the 2nd shell (Period 2).
- Mg has its outermost electrons in the 3rd shell (Period 3).
- P has its outermost electrons in the 3rd shell (Period 3).
- Ne has its outermost electrons in the 2nd shell (Period 2).
Thus, Mg and P are in the same Period (Period 3).
SECTION – III
Each one carries 6 marks
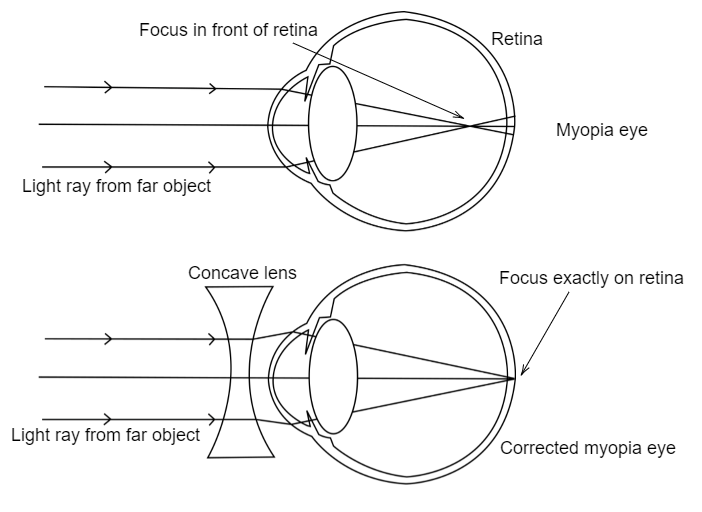
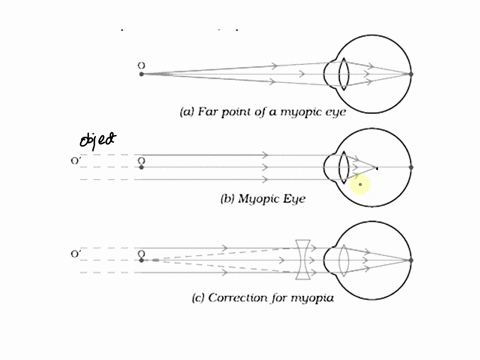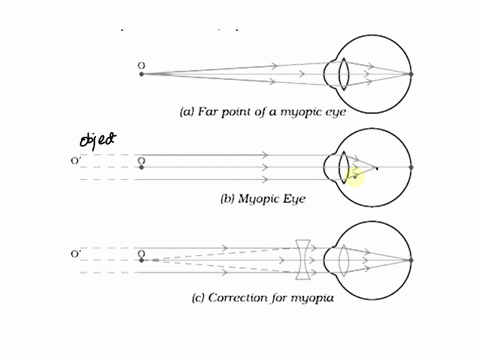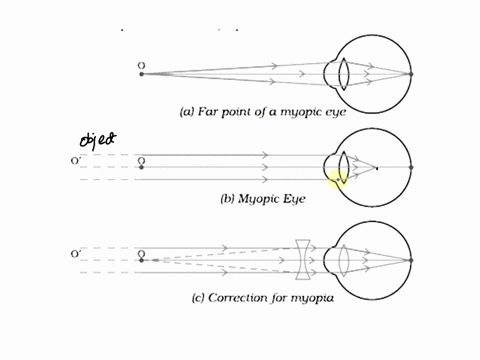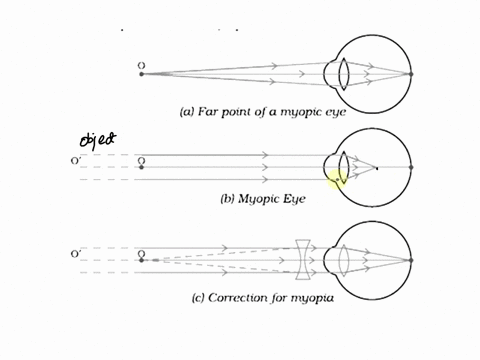
7. Draw the diagrams showing Myopia and its correction.
Myopia (Nearsightedness) occurs when the eye lens focuses light in front of the retina, making distant objects appear blurry. This happens due to either an elongated eyeball or overly curved cornea.
Diagram of Myopia:
Correction for Myopia: Myopia can be corrected with a concave lens (divergent lens), which spreads the light before it enters the eye, moving the focus onto the retina.
Diagram of Corrected Myopia:
8. Write the required material for the experiment to show that the ratio V/I is a constant for a conductor. Explain the procedure of the experiment.
Materials Required:
- A conductor (e.g., a piece of wire like copper)
- Voltmeter
- Ammeter
- Power source (e.g., battery)
- Rheostat (to vary current)
- Connecting wires
Procedure:
- Set up the circuit as follows:
- Connect the conductor (wire) in series with an ammeter to measure current (I).
- Connect a voltmeter in parallel with the conductor to measure the potential difference (V).
- Attach a rheostat to control the current.
- Use a battery as the power source.
- Adjust the Rheostat: Vary the current by adjusting the rheostat. Record the readings of the ammeter (current, I) and the voltmeter (voltage, V) for different settings of the rheostat.
- Plot the Graph: For each reading, calculate the ratio of voltage (V) to current (I). Plot a graph of voltage (V) on the y-axis and current (I) on the x-axis.
- Observe the Result: If the conductor obeys Ohm’s Law, the graph will be a straight line. The ratio
will remain constant and represent the resistance (R) of the conductor.
Conclusion: Since the ratio
is constant, the conductor follows Ohm’s law, implying it has a constant resistance.
9. Hydrogen reacts with Oxygen to produce water. What will be the mass of water produced if 100 grams of Hydrogen participated in the reaction? Calculate the number of molecules of water produced in this reaction.
Balanced Chemical Equation:
Given:
- Mass of hydrogen = 100 g
- Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) = 1 u
- Atomic mass of oxygen (O) = 16 u
Step 1: Calculate moles of hydrogen
The molar mass of hydrogen (H₂) is:
The number of moles of hydrogen:
Step 2: Use the stoichiometry of the reaction
From the balanced equation, 2 moles of H₂ produce 2 moles of H₂O. Therefore, 50 moles of H₂ will produce 50 moles of H₂O.
Step 3: Calculate the mass of water produced
The molar mass of water (H₂O) is:
The mass of water produced:
Step 4: Calculate the number of molecules of water produced
Avogadro’s number (the number of molecules per mole) is
molecules per mole.
The number of molecules of water produced:
Conclusion:
- The mass of water produced is 900 g.
- The number of molecules of water produced is
molecules.