2023 – Biology
MARKS : 40
SECTION – I
Each one Carries 2 Marks
1. Write two materials required to conduct an experiment to prove Sunlight is essential for Photosynthesis.
- A potted plant.
- Aluminum foil (or black paper to cover a part of the leaf).
2. Name two fossil fuels that are used in daily life.
- Petrol (used in vehicles).
- Natural Gas (used for cooking and heating).
3. What will happen if there is no mucus in the Oesophagus?
If there is no mucus in the oesophagus:
- Food will not move smoothly through the oesophagus as mucus provides lubrication.
- Swallowing would become painful or difficult due to increased friction between the food and the oesophageal walls.
- The inner lining of the oesophagus may get damaged due to the friction caused by dry or coarse food.
SECTION – II
Each one Carries 4 Makrs
4. Write four differences between arteries and veins.
| Feature | Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of Blood Flow | Carry blood away from the heart. | Carry blood toward the heart. |
| Oxygen Content | Usually carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary arteries). | Usually carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins). |
| Wall Structure | Thick, elastic, and muscular walls to withstand high pressure. | Thin, less elastic walls with valves to prevent backflow. |
| Blood Pressure | High pressure. | Low pressure. |
5. Name any four secondary metabolites that are used in daily life and write their uses.
- Alkaloids (e.g., Morphine): Used as painkillers in medicine.
- Tannins: Used in the leather tanning industry and as astringents in medicine.
- Terpenoids (e.g., Menthol): Used in perfumes and as flavoring agents.
- Flavonoids: Used as antioxidants in food and pharmaceuticals.
6. Observe the following table and answer the questions.
| Vitamin | Deficiency Disease | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Thiamin | Beriberi | Vomiting, difficulty in breathing. |
| Retinol | Eye-related diseases | Night blindness, cornea failure, xerophthalmia. |
| Tocoferol | Fertility-related disorders | Sterility in males, abortions in females. |
| Niacin | Pellagra | Dermatitis, diarrhea, loss of memory. |
(A) Answer the following questions based on the given table:
(i) Name two water-soluble vitamins from the table:
- Thiamin (Vitamin B1)
- Niacin (Vitamin B3)
(ii) Write two fat-soluble vitamins from the table:
- Retinol (Vitamin A)
- Tocoferol (Vitamin E)
(iii) Which vitamin from the given table is called ‘Vitamin E’?
- Tocoferol
(iv) Write any one deficiency disease caused due to the deficiency of Vitamin ‘A’:
- Night blindness
SECTION – III
Each one Carries 6 Marks
7. Explain the various stages of Mitosis.
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells. It consists of the following stages:
- Prophase:
- Chromosomes condense and become visible as two chromatids joined by a centromere.
- The nuclear membrane begins to break down.
- Spindle fibers start forming from the centrioles.
- Metaphase:
- Chromosomes align at the cell’s equatorial plane (metaphase plate).
- Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
- Anaphase:
- The centromeres split, and sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibers.
- This ensures each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
- Telophase:
- Chromatids arrive at the poles and decondense back into chromatin.
- The nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes.
- Spindle fibers disassemble.
- Cytokinesis:
- The cytoplasm divides, forming two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
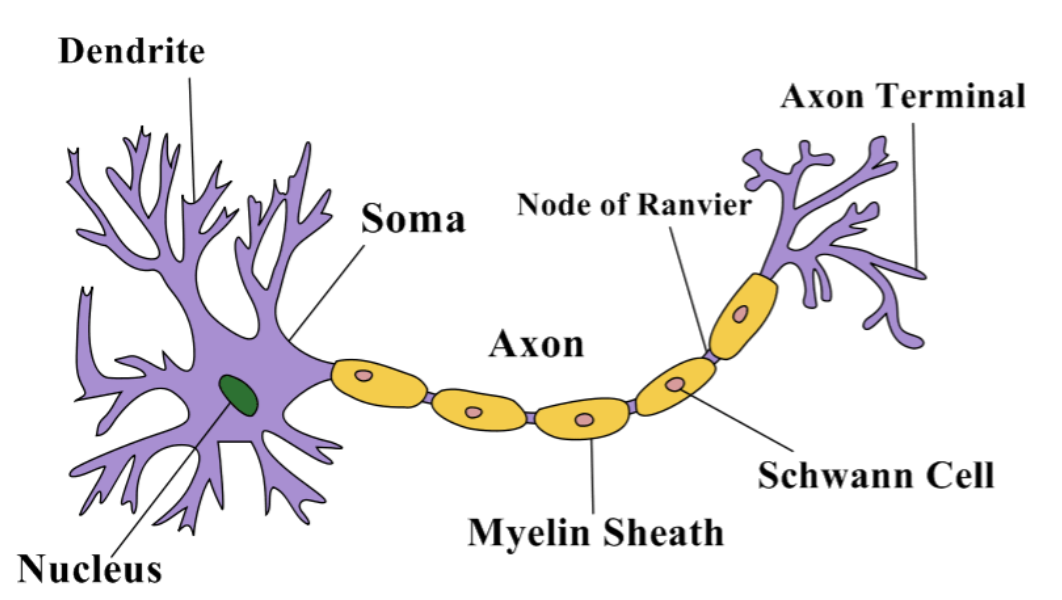
8. Draw a labelled diagram of a Nerve Cell and explain the structure.
Structure of a Nerve Cell:
- Cell Body (Soma): Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. It is responsible for the metabolic activities of the neuron.
- Dendrites: Short, branched projections that receive signals from other neurons or sensory receptors.
- Axon: A long, slender projection that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
- Myelin Sheath: A fatty layer that insulates the axon, speeding up the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Nodes of Ranvier: Gaps in the myelin sheath that facilitate the rapid conduction of impulses.
- Axon Terminals: The ends of the axon where the nerve impulse is transmitted to another neuron or effector cell.
9. Explain the procedure and results of the experiment that proves “Heat is released during Respiration”.
Procedure:
- Take two thermos flasks (one labeled as ‘Germinating seeds’ and the other as ‘Boiled seeds’).
- Place moist, germinating seeds in one flask and boiled seeds in the other flask. Ensure the flasks are airtight with cotton plugs.
- Insert a thermometer into each flask and note the initial temperature.
- After 24–48 hours, observe the temperature in both flasks.
Observations:
- The temperature in the flask with germinating seeds increases significantly.
- The temperature in the flask with boiled seeds remains constant.
Results:
The rise in temperature in the flask with germinating seeds indicates that heat is released during respiration. Germinating seeds perform cellular respiration actively, converting glucose into energy, while boiled seeds are dead and do not respire.
