PHYSICAL EDUCATION (048) Sample Paper Class XII (2024-25)
TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS MAX. MARKS: 70
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
- The question paper consists of 5 sections and 37 Questions.
- Section A consists of question 1-18 carrying 1 mark each and is multiple choice questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Sections B consist of questions 19-24 carrying 2 marks each and are very short answer types and should not exceed 60-90 words. Attempt any 5.
- Sections C consist of Question 25-30 carrying 3 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 100-150 words. Attempt any 5.
- Sections D consist of Question 31-33 carrying 4 marks each and are case studies. There is internal choice available.
- Section E consists of Question 34-37 carrying 5 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 200-300 words. Attempt any 3.
(SECTION -A)
Q1. How many total matches will be played in a knock out fixture of 19 teams?
A. 18 B. 17 C. 20 D. 16
Answer:
To determine the number of matches in a knockout tournament, you can use the formula:
Number of Matches = Number of Teams – 1
Therefore, for 19 teams:
Number of Matches = 19 – 1 = 18
Correct Answer: A
Q2. Given below are the two statements labeled Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option from the options given below:
Assertion (A): The knock out tournament is an elimination tournament.
Reason (R): In knock out tournament, the winner of each match advances in the tournament and the loser gets eliminated.
In the context of the above two statements, which one of the following is correct?
A. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). B. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). C. (A) is true, but (R) is false. D. (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
- Assertion (A) is true: Knock-out tournaments are indeed elimination tournaments.
- Reason (R) is true: This accurately describes the elimination process in knock-out tournaments.
Correct Answer: A
Q3. Match the following:
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| I. Knock Knee | 1. Increase exaggeration of backward curve |
| II. Kyphosis | 2. Wide gap between the knees when standing with feet together |
| III. Lordosis | 3. Knees touch each other in normal standing position |
| IV. Bow legs | 4. Inward curvature of the spine |
A. I-3, II-1, III-4, IV-2 B. I-1, II-3, III-4, IV-2 C. I-4, II-2, III-1, IV-3 D. I-2, II-3, III-4, IV-1
Answer:
- Knock Knee (I): Knees touch each other in normal standing position.
- Kyphosis (II): Increase exaggeration of backward curve (often referred to as “hunchback”)
- Lordosis (III): Inward curvature of the spine (often referred to as “swayback”)
- Bow Legs (IV): Wide gap between the knees when standing with feet together.
Correct Answer: D
Q4. For developing muscles, which nutrient should be increased in the diet?
A. Vitamins B. Protein C. Minerals D. Carbohydrates
Answer:
Protein is the primary nutrient for muscle growth and repair.
Correct Answer: B

Q5. Identify the asana:
A. Paschimottanasana B. Halasana C. Vajrasana D. Dhanurasana
Answer:
A. Paschimottanasana
Q6. Which asana is pose like cobra?
A. Bhujangasana B. Dhanurasana C. Vajrasana D. Ardhmatsyendrasana
Answer: A. Bhujangasana (also known as the Cobra Pose)
Q7. Deaflympics Games was first organized in the year…………
A. 1896 B. 1960 C. 1924 D. 1951
Answer: D. 1951
Q8. Menarche is defined as the:
A. Ending of menstrual period of women B. Beginning of menstrual period in women C. Time of pregnancy D. Missing of menstrual cycle
Answer: B. Beginning of menstrual period in women
Q9. Which of the following are fat-soluble vitamins?
A. Vitamin D & K B. Vitamin B & C C. Vitamin A & E D. Both option a & c
Answer: D. Both option a & c (Vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble)
Q10. Match the following:
I. Plate Tapping Test | 1. Upper body strength boys II. Push-up | 2. Reaction time III. Partial Curl-up | 3. Upper body strength girls IV. Modified push-up | 4. Abdominal strength
A. I-2, II-1, III-4, IV-3 B. I-2, II-3, III-1, IV-4 C. I-1, II-3, III-2, IV-4 D. I-2, II-3, III-4, IV-1
Answer: A. I-2, II-1, III-4, IV-3
Q11. Which of the following is a physiological factor determining flexibility?
A. Bone density B. Joint structure C. Cardiac output D. Tidal Volume
Answer: B. Joint structure
Q12. The ability to tolerate higher concentrations of ……………. can help in improving endurance performance.
A. Lactic acid B. Hydrochloric acid C. Acetic acid D. Sulphuric acid
Answer: A. Lactic acid
Q13. If a ball is hit and it is stopped by gravitational force, this is an example of which law of Motion?
A. Law of Inertia B. Law of acceleration C. Law of action and reaction D. Both a & b
Answer: C. Law of action and reaction (Gravity exerts an upward force on the ball, and the ball exerts an equal and opposite force on the Earth)
Q14. In which of the following sports does friction play the least important role?
A. Car race B. Football C. Ice skating D. Hockey
Answer: C. Ice skating (Ice skating relies on minimizing friction for smooth movement)
Q15. Instrumental aggression is related to:
A. Accepting defeat B. Achieving goal C. Only performance D. Hurting someone to gain something
Answer: D. Hurting someone to gain something
Q16. Given below are the two statements labeled Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Aggression is part of human behavior and is necessary for an individual to live and struggle for higher achievements.
Reason (R): Aggression is inevitable and inseparable in sport activities.
In the context of the above two statements, which one of the following is correct?
A. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). B. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). C. (A) is true, but (R) is false. D. (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer: B. Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). (Aggression can be a part of human behavior, but it’s not always necessary for achievement, and it’s not always inevitable or inseparable in sports)
Q17. Which of these is a type of endurance?
A. Static B. Specific C. Dynamic D. Relative
Answer: B. Specific (e.g., cardiovascular endurance, muscular endurance)
Q18. Which type of coordinative ability is required in games like judo and wrestling?
A. Orientation ability B. Coupling ability (combining different movements) C. Adaptation ability D. Differentiation ability
Answer: B. Coupling ability
Q19. Enlist any two exercise guidelines by WHO for different age groups.
- Children (5-17 years): Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous-intensity physical activity daily.
- Adults (18-64 years): Perform at least 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity throughout the week, or 75-150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic activity.
Q20. How can we say that protein is an essential component of diet?
Protein is an essential component of the diet because:
- Building and repairing tissues: It forms the building blocks of all body tissues, including muscles, organs, and skin.
- Enzyme production: Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions in the body.
- Hormone production: Many hormones, such as insulin and growth hormone, are made of protein.
- Immune system function: Antibodies, which fight off infections, are proteins.
- Energy source: While not the primary source, protein can be used as an energy source when carbohydrate and fat stores are low.
Q21. Mention the test performed on 9 to 18 yrs. of age group in SAI Khelo India fitness test and explain any one?
- Standing Broad Jump:
- 600m Run/Walk
- Partial Curl-up
- Plate Tapping Test
- Push-up
- Modified Push-up
Explanation of Partial Curl-up:
- This test assesses abdominal strength.
- The individual lies on their back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Hands are placed behind the head with fingers interlocked.
- The individual curls their upper body upwards until their shoulder blades touch the floor.
- The number of repetitions performed within a set time (usually 30 seconds) is counted.
Q22. List down the types of bone injuries.
- Fractures: A complete or partial break in the bone.
- Sprains: An injury to a ligament (the tissue that connects bones).
- Strains: An injury to a muscle or tendon (the tissue that connects muscle to bone).
- Dislocations: When a bone is forced out of its normal position at a joint.
- Osteoporosis: A disease that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
Q23. What do you understand by the term goal setting?
Goal setting is the process of defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
- Motivation: Provides a sense of purpose and direction.
- Focus: Helps to concentrate efforts on achieving specific outcomes.
- Performance improvement: Sets a standard to measure progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Increased self-confidence: Achieving goals boosts self-esteem and motivation.
Q24. Define Flexibility and list down its type.
Definition: Flexibility is the range of motion of a joint or series of joints, which can be measured in degrees of a circle. It is influenced by factors like age, gender, and physical activity level.
Types of Flexibility:
- Static Flexibility: The ability to hold an extended position at one point in the range of motion. (e.g., sit-and-reach test)
- Dynamic Flexibility: The ability to move a joint through its full range of motion with speed and force. (e.g., swinging a leg)
Q25. Specify the purpose of specific sports programs organized for community services.
Specific sports programs organized for community services serve several important purposes:
-
Promoting Health and Well-being:
- Increase physical activity levels within the community.
- Reduce the prevalence of chronic diseases like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
- Improve mental health and reduce stress levels.
-
Social Development:
- Foster social interaction and build community bonds.
- Provide opportunities for teamwork, cooperation, and leadership.
- Reduce social isolation and promote inclusivity.
-
Skill Development:
- Develop motor skills, coordination, and agility.
- Enhance sportsmanship, discipline, and fair play.
- Provide opportunities to learn new skills and develop talents.
- Develop motor skills, coordination, and agility.
-
Community Development:
- Create safe and accessible recreational spaces for the community.
- Improve the overall quality of life in the community.
- Address specific social issues like youth crime and substance abuse.
Q26. What are the health problems faced by a woman due to the female athlete triad in its sports and athletic performance?
The female athlete triad is a syndrome characterized by three interrelated conditions:
-
Disordered Eating:
- Restrictive eating patterns, such as calorie restriction or excessive dieting.
- May lead to nutrient deficiencies, low energy availability, and impaired metabolic function.
- Restrictive eating patterns, such as calorie restriction or excessive dieting.
-
Amenorrhea:
- Absence of menstrual periods for three or more consecutive months.
- Can be caused by low energy availability and hormonal imbalances
- Increases the risk of bone loss and osteoporosis.
-
Osteoporosis:
- Low bone mineral density, making bones more susceptible to fractures.
- Caused by hormonal imbalances and insufficient calcium intake.
- Low bone mineral density, making bones more susceptible to fractures.
Health problems in sports and athletic performance:
- Reduced performance: Low energy levels, fatigue, muscle weakness, and impaired cognitive function can negatively impact athletic performance.
- Increased injury risk: Bone weakness increases the risk of stress fractures and other injuries.
- Psychological issues: Disordered eating and body image concerns can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Q27. Write in detail the aims and objectives of Special Olympics Bharat.
Aims:
- To provide year-round sports training and athletic competition in a variety of Olympic-type sports for children and adults with intellectual disabilities.
- To promote the acceptance and inclusion of people with intellectual disabilities in their communities.
Objectives:
- Enhance physical fitness and well-being: Improve motor skills, coordination, and overall health through regular physical activity.
- Develop social skills: Foster teamwork, cooperation, and sportsmanship.
- Build self-confidence and esteem: Provide opportunities for achievement and recognition.
- Promote understanding and acceptance: Raise awareness about intellectual disabilities and challenge negative stereotypes.
- Provide leadership opportunities: Empower individuals with intellectual disabilities to become leaders and role models.
Q28. Differentiate between nutritive and non-nutritive components of a diet on the basis of their functions.
Nutritive Components:
-
Functions:
- Provide essential nutrients for growth, development, and bodily functions.
- Supply energy for daily activities.
- Maintain and repair tissues.
- Support immune function.
-
Examples:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
Non-nutritive Components:
-
Functions:
- Do not provide essential nutrients.
- May contribute to taste, flavor, and texture.
- Can have positive or negative effects on health.
-
Examples:
- Fiber
- Phytochemicals
- Antioxidants
- Additives (colors, flavors, preservatives)
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
Q29. With the help of suitable sports examples, explain the application of Newton’s Third Law in sports.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- Swimming: When a swimmer pushes against the water (action), the water pushes back with an equal and opposite force, propelling the swimmer forward.
- High Jump: The athlete pushes down on the ground (action), and the ground pushes back up with an equal and opposite force, helping them to achieve greater height.
- Tennis: When a tennis player hits the ball with the racquet (action), the ball exerts an equal and opposite force on the racquet.
- Rowing: Rowers pull on the oars (action), and the oars push against the water, propelling the boat forward.
Q30. How can we enhance performance with the help of self-talk and self-esteem?
Self-Talk:
- Positive self-talk: Using encouraging and motivating phrases can boost confidence and focus. For example, “I can do this,” or “I am strong and capable.”
- Instructional self-talk: Using specific cues to guide performance. For example, “Keep your eye on the ball,” or “Follow through with your swing.”
- Negative self-talk: Can be detrimental to performance, leading to anxiety and self-doubt.
It’s important to identify and replace negative thoughts with positive ones.
Self-Esteem:
- Building self-esteem: Recognizing and celebrating achievements, both big and small.
- Focusing on strengths and areas for improvement: Identifying and working on areas for growth can boost confidence.
- Setting realistic goals: Achieving goals, no matter how small, can enhance self-esteem.
- Learning from mistakes: Viewing setbacks as learning opportunities can help build resilience and self-confidence.
By using positive self-talk and building self-esteem, athletes can improve their mental game, enhance their focus, and ultimately achieve their performance goals.
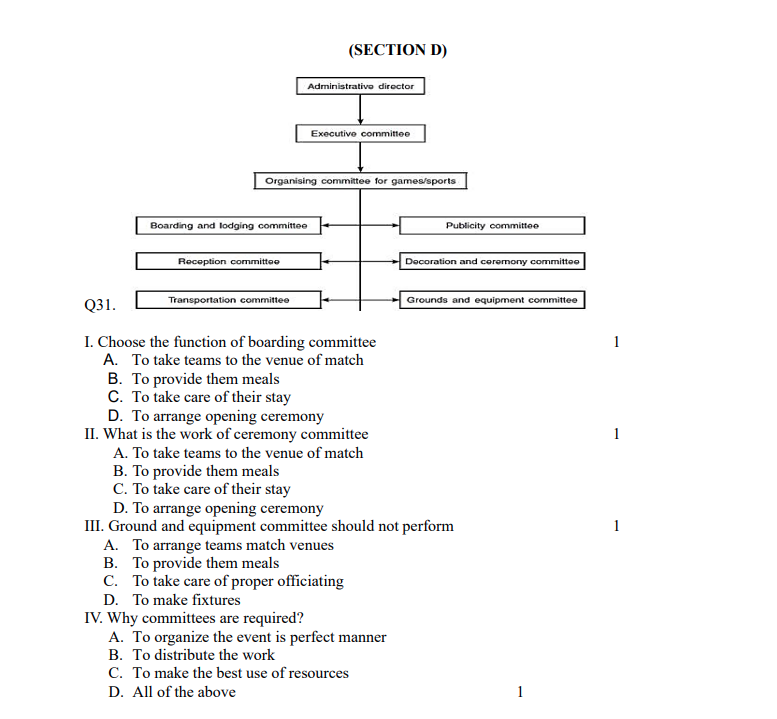
Certainly! Here are the questions and options along with the answers, based on the provided organizational chart:
Q31. I. Choose the function of the boarding committee.
A. To take teams to the venue of match B. To provide them meals C. To take care of their stay D. To take care of their travel
Answer: C. To take care of their stay
II. What is the work of the ceremony committee?
A. To take teams to the venue of match B. To provide them meals C. To take care of their stay D. To arrange the opening ceremony
Answer: D. To arrange the opening ceremony
III. The Ground and Equipment committee should not perform:
A. To arrange proper match venues B. To provide them meals C. To arrange and maintain the ground D. To arrange and maintain equipment
Answer: B. To provide them meals
IV. Why are committees required?
A. To organize the event in a perfect manner B. To distribute the work C. To make the best use of resources D. All of the above
Answer: D. All of the above
Questions for Visually Impaired
Ram is a secretary of the state basketball association. He has been given the responsibility to organize a subjunior national tournament. He wants to organize the event at a large scale and start distributing the work in various committees. He delegates the duties to different individuals with authority and responsibility.
(Answer the following questions on the basis of the above paragraph)
I. Which committee is responsible to make the event awareness?
A. Publicity Committee B. Hospitality C. Registration committee D. Transports
Answer: A. Publicity Committee
II. ………………. is the process of identifying and grouping the work to be performed.
A. Planning B. Directing C. Organizing D. Controlling
Answer: C. Organizing
III. The reception committee for the tournament is responsible for ________
A. Welcoming the participants B. Arranging accommodation and meals for the participants C. Proper upkeep of the venues
Answer: A. Welcoming the participants
IV. If the responsibility of a committee is to fix venue, date and timing of the sports events, it is a ________
A. Post meeting committee B. Pre meet committee C. During meet committee D. All the above
Answer: B. Pre meet committee

Q32.
I. The first Paralympics was organized in:
A. 1960 B. 1970 C. 1965 D. 1985
Answer: C. 1965
II. Special education is a branch of education that deals with:
A. Educating children in special schools B. Instructions designing for students with special needs C. To provide opportunity of special education D. More than one of the above
Answer: B. Instructions designing for students with special needs
III. Why is it called the Paralympics?
A. The first competition was held in Paraguay B. It was originally for paramilitary soldiers injured in WW2 C. The event runs parallel with the Olympics D. It’s an event for paraplegics
Answer: B. It was originally for paramilitary soldiers injured in WW2
IV. What is the motto of the Paralympic Games?
A. Spirit in motion B. Citius, Altius, Fortius” C. “Faster, Higher, Stronger” D. Diversity, Equality, Inclusion”
Answer: D. Diversity, Equality, Inclusion”
(Question for Visually Impared)
Paragraph:
The Paralympic Games are a major international multi-sport event involving athletes with a range of physical disabilities, including impaired muscle power,
Questions:
I. What is the primary focus of the Paralympic Games?
A. To promote physical fitness among children B. To involve athletes with a range of physical disabilities in competitive sports C. To honor the history of the Olympic Games D. To raise funds for sports organizations
II. Who organized the first event that eventually led to the creation of the Paralympic Games?
A. Pierre de Coubertin C. Lord Zeus B. Dr. Ludwig Guttmann D. Norabji Tata
III. In which year were the first official Paralympic Games held?
A. 1948 C. 1960 B. 1952 D. 1960
IV. Where were the first official Paralympic Games held?
A. Tokyo, Japan C. Rome, Italy B. London, United Kingdom D. Sydney, Australia
Answers:
I. B. To involve athletes with a range of physical disabilities in competitive sports
II. B. Dr. Ludwig Guttmann
III. D. 1960
IV. C. Rome, Italy

Q33. I. What is the primary effect of exercise on the cardiorespiratory system?
A. Decreased heart rate B. Increased stroke volume C. Decreased lung capacity D. Decreased blood pressure
Answer: B. Increased stroke volume
II. What is stroke volume?
A. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per minute B. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per beat C. The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole D. The volume of blood pumped by the heart during exercise
Answer: B. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per beat
III. Cardiac output is
A. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per minute B. The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole C. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per beat D. The volume of blood pumped by the heart during exercise
Answer: A. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per minute
IV. Blood pressure is
A. The volume of blood ejected by the heart per minute B. The force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries C. The rate of blood flow through the veins D. The amount of oxygen carried by red blood cells
Answer: B. The force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries
Certainly, here is the passage and the questions with options and answers for the visually impaired:
Passage:
Ramesh is an athlete of XYZ school. He is used to doing the 100-meter event for his school. He used to work hard throughout the year to get his best performance. One day he got injured in the winter season due to improper warming-up. He has been given first-aid before being sent to the hospital.
Questions:
I. Sprain is an injury of …
A. Ligament B. Muscle C. Bone D. Joint
Answer: A. Ligament
II. In PRICE treatment, I stands for
A. Iceing B. Incline C. Incision D. Irritation
Answer: A. Iceing
III. Abrasion is a
A. Type of fracture B. Joint dislocation C. Soft tissue injury D. Internal injury
Answer: C. Soft tissue injury
IV. Why is warming up necessary?
A. To avoid injuries B. To increase body temperature C. To increase pulse rate D. All the above
Answer: D. All the above
Q34. List down any four asanas used for prevention of Hypertension. Explain the procedure, benefits, and contraindications of any one of them with the help of a stick diagram.
Four asanas for hypertension prevention:
- Anulom Vilom Pranayama (Alternate Nostril Breathing): Helps regulate blood pressure and calm the nervous system.
- Shavasana (Corpse Pose): Promotes relaxation and reduces stress, which can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Dhanurasana (Bow Pose): Improves blood circulation and strengthens the heart.
- Viparita Karani (Legs-Up-the-Wall Pose): Helps to improve blood flow to the heart and reduce stress on the legs.
Explanation of Anulom Vilom Pranayama:
Procedure:
- Sit comfortably in Sukhasana (Easy Pose) or Padmasana (Lotus Pose).
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Inhale deeply through your left nostril.
- Close your left nostril with your ring finger and release the right thumb.
- Exhale slowly through your right nostril.
- Inhale deeply through your right nostril.
- Close your right nostril with your thumb and release your ring finger.
- Exhale slowly through your left nostril.
- Continue this cycle for 5-10 minutes.
Benefits:
- Reduces stress and anxiety: Helps to calm the mind and reduce the fight-or-flight response.
- Regulates blood pressure: Balances the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate and blood pressure.
- Improves respiratory function: Increases lung capacity and oxygen intake.
- Increases focus and concentration: Calms the mind and improves mental clarity.
Contraindications:
- Avoid during pregnancy and menstruation.
- People with severe sinusitis or nasal congestion should avoid this practice.
(Note: Since this is a text-based environment, I cannot provide a stick diagram. However, you can easily find visual representations of Anulom Vilom Pranayama online or in yoga books.)
Q35. Discuss the purpose of Rikli & Jones fitness test and explain the procedure of any two test batteries in detail.
Purpose of Rikli & Jones Fitness Test:
The Rikli & Jones Fitness Test is a battery of tests designed to assess the physical fitness levels of older adults. It focuses on functional fitness, measuring abilities that are crucial for maintaining independence and quality of life in daily activities.
Two test batteries in detail:
- Chair Stand Test:
- Purpose: To assess lower body strength.
- Procedure:
- The individual sits on a chair with their back against the chair back.
- They cross their arms across their chest.
- They stand up completely and then sit back down without using their hands for support.
- The number of repetitions completed in 30 seconds is counted.
- Arm Curl Test:
- Purpose: To assess upper body strength.
- Procedure:
- The individual sits on a chair with their back against the chair back.
- They hold a light weight (usually a 4-pound or 5-pound weight) in one hand.
- They bend their elbow, bringing the weight towards their shoulder.
- They then straighten their arm.
- The number of repetitions completed in 30 seconds is counted.
- The test is performed with both arms.
Q36. Define strength and differentiate between Isometric, Isotonic, and Isokinetic exercises.
Definition of Strength:
Strength is the ability of a muscle or muscle group to exert force against resistance. It is a crucial component of overall physical fitness and is essential for daily activities, sports performance, and maintaining good health.
Differentiation between Isometric, Isotonic, and Isokinetic Exercises:
- Isometric Exercises:
- Muscle contraction occurs without any change in muscle length.
- Examples: Pushing against a wall, holding a plank position.
- Isotonic Exercises:
- Muscle contraction occurs with a change in muscle length.
- Examples: Lifting weights, running, jumping.
- Concentric contraction: Muscle shortens (e.g., lifting a weight).
- Eccentric contraction: Muscle lengthens (e.g., lowering a weight).
- Isokinetic Exercises:
- Muscle contraction occurs at a constant speed.
- Requires specialized equipment that provides resistance throughout the full range of motion.
- Examples: Isokinetic dynamometers.
Q37. What are the various types of friction? With the help of suitable examples, explain why friction is necessary in sports.
Types of Friction:
- Static Friction: The force that prevents an object from moving when a force is applied to it.
- Kinetic Friction: The force that opposes the motion of an object that is already moving.
- Rolling Friction: The force that opposes the motion of a rolling object.
- Fluid Friction: The force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid (like air or water).
Why friction is necessary in sports:
- Running and Jumping: Friction between the athlete’s shoes and the ground provides traction, allowing for acceleration, deceleration, and changes in direction. Without friction, athletes would slip and fall.
- Throwing and Striking: Friction between the hand and the ball or implement (e.g., bat, racket) allows for the transfer of force and generates speed.
- Wrestling and Judo: Friction is essential for maintaining a grip and exerting force on an opponent.
- Swimming: Friction with the water propels the swimmer forward.
- Cycling: Friction between the tires and the road provides traction and allows for efficient pedaling.
