GEOGRAPHY (029)
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
Class: XII: 2024 – 25
Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them:
(i) This questions paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Question paper is divided into five sections A, B, C, D and E.
(iii) Section A Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice type questions. Each question carries
1 mark.
(iv) Section B Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source-based questions. Each question carries 3
marks.
(v) Section C Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries
3 marks. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
(vi) Section D Questions no. 24 to 28 are Long Answer type questions. Each question carries
5 marks. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
(vii) Section E Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-based questions. Each question carries 5
marks.
(viii) In addition to this, NOTE that a separate question has been provided for Visually Impaired
candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, map etc. Such questions are to be
attempted by Visually Impaired candidates only.
(ix) There is no overall choice given in the question paper. However, an internal choice has
been provided in a few questions in all sections other than Section A.
Section A – Multiple Choice Type Questions (1 mark each)
1. The Human Poverty Index measures the shortfall in human development on the basis of which parameter/s?
A. The adult literacy rate and the life expectancy at birth.
B. Access to resources in terms of purchasing power.
C. The number of small children who are underweight.
D. The number of children enrolled in the school.
Answer: A. The adult literacy rate and the life expectancy at birth.
2. There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below.
Assertion (A): Often smaller countries have done better than larger ones and relatively poorer nations have been ranked higher than richer neighbours in terms of human development.
Reason (R): Size of the territory and per capita income are not directly related to human development. Countries with higher human development are those where a lot of investment in the social sector has taken place.
Options:
A. Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
B. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
C. Both (A) and (R) are incorrect.
D. (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
Answer: B. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
3. Which of the following statements are correct related to rural marketing centres?
Choose the correct option.
i. Rural marketing centres cater to nearby settlements.
ii. Rural Marketing centres are quasi-urban trading centres of the most rudimentary type.
iii. They offer manufactured goods as well as many specialized markets develop, e.g., markets for labour, housing, semi or finished products.
iv. Personal and professional services are not well-developed. These form local collecting and distributing centres.
Options:
A. i, ii, iv
B. i, iii, iv
C. ii, iii, iv
D. i, ii, iii
Answer: D. i, ii, iii
4. Arrange the following facts related to the history of international trade in sequence.
i. The Silk Route is an early example of long distance trade connecting Rome to China – along the 6,000 km route.
ii. After the disintegration of the Roman Empire, European commerce grew during twelfth and thirteenth century with the development of ocean-going warships. Trade between Europe and Asia grew and the Americas were discovered.
iii. Fifteenth century onwards, European colonialism began and along with trade of exotic commodities, a new form of trade emerged which was called slave trade.
iv. During the World Wars I and II, countries imposed trade taxes and quantitative restrictions for the first time.
Codes:
A. i, ii, iv, v
B. iv, ii, iii, i
C. i, ii, iii, iv
D. iii, ii, iv, i
Answer: C. i, ii, iii, iv
5. The act of opening up economies for trading by bringing down trade barriers like tariffs and allowing goods and services from everywhere to compete with domestic products and services is called:
A. Dumping
B. Trade liberalization
C. Balance of trade
D. Bilateral trade
Answer: B. Trade liberalization
6. Arrange the following states in order of their population from highest to lowest.
- Bihar
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
Codes:
A. 1, 3, 2, 4
B. 4, 3, 2, 1
C. 3, 2, 1, 4
D. 2, 1, 4, 3
Answer: C. 3, 2, 1, 4
7. There are four distinct phases of population growth identified in India over the last one century. Identify the phase from the given description.
This period is referred to as the period of population explosion in India, which was caused by a rapid fall in the mortality rate but a high fertility rate of population in the country. The average annual growth rate was as high as 2.2 percent. It is in this period that developmental activities were introduced through a centralized planning process, and the economy started showing up, ensuring the improvement of living conditions of people at large. Consequently, there was a high natural increase and higher growth rate.
A. Phase I 1901-1921
B. Phase II 1921-1951
C. Phase III 1951-1981
D. Phase IV post 1981 till present
Answer: C. Phase III 1951-1981
8. The objective of protective irrigation is to___________________:
A. protect the crops from adverse effects of soil moisture deficiency.
B. provide sufficient soil moisture in the cropping season to achieve high productivity.
C. double water input per unit area of cultivated land so that multiple cropping can be done.
D. increase the productivity of soil.
Answer: A. protect the crops from adverse effects of soil moisture deficiency.
9. There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below.
Assertion (A): There has been a significant increase in agricultural output and yield, of many crops such as rice and wheat among the other crops like sugarcane, oilseeds, and cotton, due to improvement in technology during the last 50 years.
Reason (R): Expansion of irrigation has played a crucial role in enhancing agricultural output in the country. It provided the basis for the introduction of modern agricultural technology during the last 50 years.
Options:
A. Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
B. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
C. Both (A) and (R) are incorrect.
D. (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
Answer: B. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
10. Identify the statement that is NOT true with regard to watershed management?
I. It refers to efficient management and conservation of surface and groundwater resources.
II. Watershed management includes judicious use of all resources – both natural and human within a watershed.
III. Watershed management aims at bringing about a balance between natural resources on the one hand and society on the other.
IV. The success of watershed development solely depends upon the state government.
Options:
A. Statement I and IV
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Statement IV
Answer: D. Statement IV
11. A group of students were conducting research on water pollution levels in Delhi. Which organization will students need to visit to gather information on water quality?
A. Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC)
B. Indian Council of Environmental Research (ICER)
C. National Water Development Agency (NWDA)
D. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
Answer: D. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
12. Which one of the following is incorrectly matched?
List I (Name of the state) – List II (Coal mining Centre)
A. West Bengal – I. Raniganj
B. Tamil Nadu – 2. Neyveli
C. Maharashtra – 3. Korba
D. Odisha – 4. Talcher
Answer: C. Maharashtra – 3. Korba
Explanation: Korba is in Chhattisgarh, not Maharashtra.
13. Satellite is a mode of communication in itself as well as it regulates the use of other means of communication. Choose the correct satellite system used by India.
- India Remote Sensing Satellite System (IRS)
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
- Indian National Satellite System (INSAT)
- India Regional Navigation Satellite System
Codes:
A. Both I and III
B. Only I
C. Both II and III
D. Only IV
Answer: A. Both I and III
14. Setubharatam Pariyojana launched by the Indian government aims to achieve?
A. Development of State roads along coastal border areas.
B. The construction of about 1500 major bridges and 200 rail over bridges and rail under bridges.
C. Development of border roads.
D. Construction of more waterways.
Answer: B. The construction of about 1500 major bridges and 200 rail over bridges and rail under bridges.
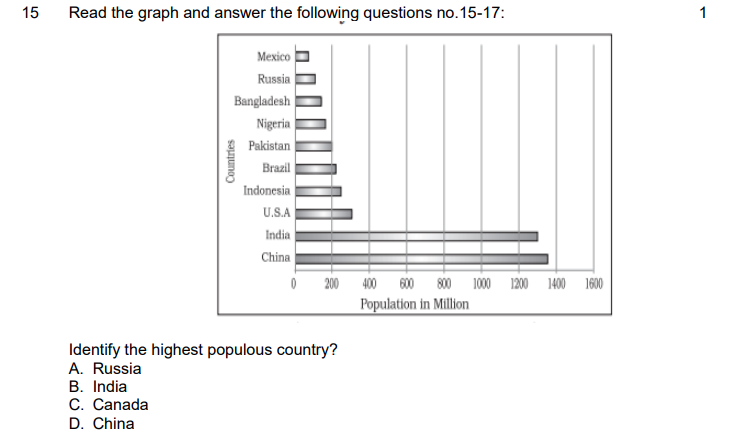
15. Identify the highest populous country?
- A. Russia
- B. India
- C. Canada
- D. China
Answer: D. China
15.1 (For Visually Impaired Candidates)
This question is the same as question 15.
16. Identify the African country that has very high population.
- A. Mexico
- B. Brazil
- C. Pakistan
- D. Nigeria
Answer: D. Nigeria
16.1 (For Visually Impaired Candidates)
- A. The total number of people living in a specific area.
- B. The arrangement or spread of people across a given area.
- C. The rate at which the population increases over time.
- D. The number of births per 1,000 people in the population.
Answer: B. The arrangement or spread of people across a given area.
17. Which continent has the highest number of the world’s most populous countries?
- A. Africa
- B. North America
- C. Asia
- D. South America
Answer: C. Asia
Question 17.1
Which continent has the highest number of the world’s most populous countries?
- A. Africa
- B. North America
- C. Asia
- D. South America
Answer: C. Asia
18. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Tourism
Tourism has become the world’s single largest tertiary activity in total registered jobs (250 million) and total revenue (40 per cent of the total GDP). Besides, many local persons are employed to provide services like accommodation, meals, transport, entertainment, and special shops serving the tourists. Tourism fosters the growth of infrastructure industries, retail trading, and craft industries (souvenirs). In some regions, tourism is seasonal because the vacation period is dependent on favourable weather conditions, but many regions attract visitors all the year round.
The warmer places around the Mediterranean Coast and the West Coast of India are some of the popular tourist destinations in the world. Others include winter sports regions, found mainly in mountainous areas, and various scenic landscapes and national parks, which are scattered. Historic towns also attract tourists because of the monuments, heritage sites, and cultural activities.
(I) What constitutes tourism?
Answer:
Tourism constitutes activities such as providing accommodation, meals, transport, entertainment, and special shops for tourists. It also includes the growth of infrastructure industries, retail trading, and craft industries (souvenirs).
(II) List two renowned global tourist destinations.
Answer:
- Mediterranean Coast
- West Coast of India
(III) “Tourism has become the largest tertiary activity in the world”. Comment.
Answer:
Tourism has become the world’s largest tertiary activity due to its significant contribution to global employment (250 million jobs) and revenue (40% of total GDP). It supports various industries such as hospitality, transportation, retail, and cultural services. This has made tourism a driving force in the global economy, affecting infrastructure development, job creation, and cultural exchange.
Question 1:
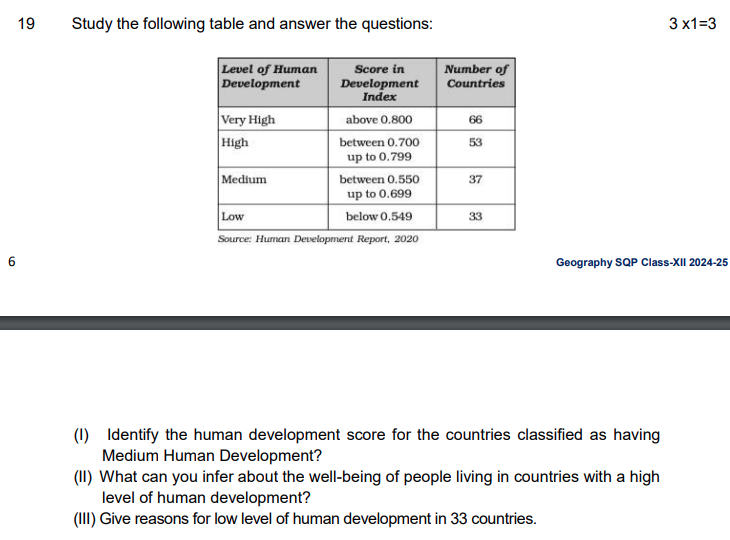
Identify the human development score for the countries classified as having Medium Human Development?
Answer:
The countries classified as having Medium Human Development have a Human Development Index (HDI) score between 0.550 and 0.699.
Question 2:
What can you infer about the well-being of people living in countries with a high level of human development?
Answer:
Countries with a high level of human development (HDI score between 0.700 and 0.799) likely exhibit a high standard of living for their citizens. This is often reflected in:
- High life expectancy: People in these countries tend to live longer, healthier lives due to better healthcare and nutrition.
- High levels of education: A high proportion of the population has access to quality education, leading to higher literacy rates and better job opportunities.
- Decent standards of living: People in these countries have access to basic necessities like food, shelter, and clean water, as well as opportunities for economic growth and social mobility.
Question 3:
Give reasons for low level of human development in 33 countries.
Answer:
Several factors can contribute to low human development (HDI score below 0.549) in a country:
- Poverty and Inequality: High levels of poverty and income inequality can limit access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.
- Conflict and Instability: Wars, civil unrest, and political instability can disrupt development efforts and displace populations, hindering progress in various areas.
- Natural Disasters: Frequent natural disasters can cause significant damage to infrastructure and livelihoods, hindering development progress.
- Lack of Access to Resources: Limited access to clean water, sanitation, and energy resources can significantly impact health and well-being.
- Environmental Degradation: Environmental issues like deforestation, pollution, and climate change can have adverse effects on health and livelihoods.
- Weak Governance and Institutions: Corruption, lack of transparency, and weak institutions can hinder effective service delivery and economic development
Section C
20. Explain humanisation of nature with the help of a real life example.
OR
“The concept of Neo-determinism is compared with traffic lights on the cross road”. Analyze the statement with examples.
Answer 1: Humanisation of Nature
Humanisation of nature refers to the way humans have modified and interacted with the natural environment to create a more lived-in and controlled environment. This concept emphasizes the transformation of the physical landscape for human use, often to meet societal needs, by altering or managing natural features. It reflects the shift from viewing nature as something independent of human action to a process where nature is shaped and influenced by human activity.
Real-life Example:
A classic example of the humanisation of nature is the construction of terraces in the hilly regions of India, such as in Himachal Pradesh or Uttarakhand. In these regions, the natural sloping terrain has been modified to create terraces for agriculture. This process involves leveling the land, constructing walls to prevent soil erosion, and adapting crops to the environmental conditions. The human action on the environment has made the land more productive for farming but also resulted in significant changes to the natural landscape.
Answer 2: Neo-determinism and Traffic Lights
Neo-determinism is a concept that emerged as a response to environmental determinism. While environmental determinism suggests that the environment strictly determines human actions and development, Neo-determinism emphasizes that humans have the ability to adapt to or modify the environment, but this adaptation is still influenced by the natural environment. This theory strikes a balance between the influence of nature and the ability of humans to shape their destiny.
Traffic Lights Analogy:
The statement “Neo-determinism is compared with traffic lights on the crossroad” uses the analogy of traffic lights to explain the relationship between humans and the environment. In this analogy:
-
The Environment (Green light): Just like the green light at a traffic signal, the environment provides humans with opportunities and constraints. The green light symbolizes the favorable conditions in nature (such as fertile land, good climate) that allow for human development and progress.
-
Human Decision (Yellow light): The yellow light in traffic signals represents a stage where humans must slow down and assess the environment. It signifies human decisions, where people must adapt to natural conditions, such as when they respond to climate change or adapt their farming methods to soil conditions.
-
Environmental Constraints (Red light): The red light symbolizes the limitations or challenges posed by the environment. In some cases, environmental factors like droughts, floods, or natural disasters limit human actions. It suggests that while humans have some control over nature, they must still respect and adjust to the natural world’s boundaries.
Example:
- In the case of agriculture, humans might have the green light to grow crops in fertile regions, but during a drought, the red light is imposed by the environment. People can adapt (yellow light) by shifting crops or investing in irrigation systems, but ultimately, nature still has an overriding influence over the potential success or failure of agricultural production.
Questions & Answers:
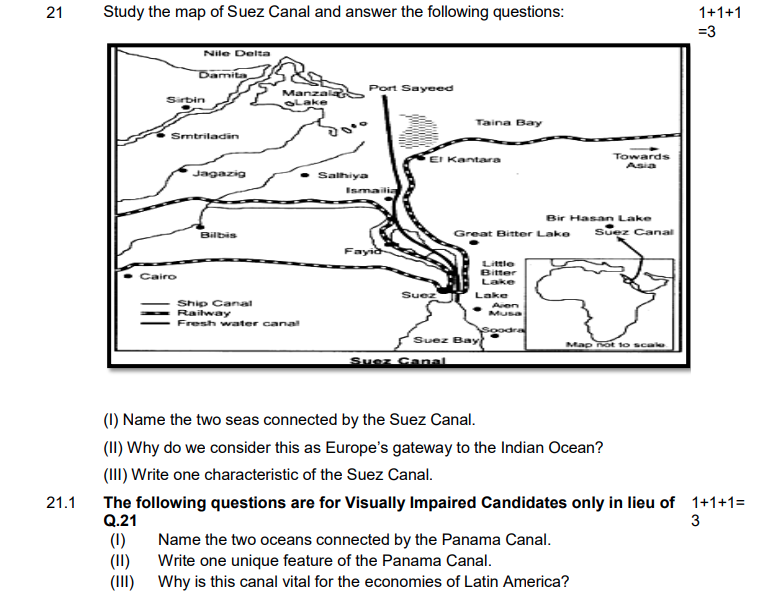
21. (1) Name the two seas connected by the Suez Canal.
Answer: The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.
21. (2) Why do we consider this as Europe’s gateway to the Indian Ocean?
Answer: The Suez Canal provides a direct and shorter route for ships traveling from Europe to the Indian Ocean, bypassing the long and arduous journey around the southern tip of Africa. This significantly reduces travel time and costs, making it a vital trade route for Europe.
21. (3) Write one characteristic of the Suez Canal.
Answer: One characteristic of the Suez Canal is its significant impact on global trade. It facilitates the movement of goods between Europe, Asia, and Africa, making it a vital link in the global supply chain.
21.1 The following questions are for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of
Q.21
21.1 (1) Name the two oceans connected by the Panama Canal.
Answer: The Panama Canal connects the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
21.1 (2) Write one unique feature of the Panama Canal.
Answer: A unique feature of the Panama Canal is its system of locks that raises and lowers ships to navigate the elevation difference between the two oceans.
21.1 (3) Why is this canal vital for the economies of Latin America?
Answer: The Panama Canal is vital for the economies of Latin America as it significantly reduces shipping times and costs between the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of the continent. This facilitates trade within Latin America and with other regions, boosting economic growth and development.
22. Prepare a proposal for a smart city that integrates advanced technology to enhance urban living while prioritising sustainability, cleanliness, and affordability.
Proposal for a Smart City:
Introduction:
A smart city aims to enhance the quality of urban living by leveraging technology to improve infrastructure, services, and sustainability while ensuring the well-being of its residents. The core focus of this proposal is on integrating advanced technologies to promote sustainability, cleanliness, and affordability, addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization.
1. Smart Infrastructure:
- Energy-efficient buildings equipped with solar panels, energy-saving lights, and green roofs to reduce carbon footprints and lower energy consumption.
- Smart transportation systems, including electric buses, bike-sharing programs, and autonomous vehicles to reduce traffic congestion and pollution.
- Smart grids for optimized energy distribution, reducing waste and ensuring affordable electricity for all residents.
2. Sustainable Waste Management:
- Smart waste bins equipped with sensors that inform municipal authorities when they are full, ensuring timely collection.
- Waste-to-energy plants that convert organic waste into energy, reducing landfill dependence and promoting clean energy production.
- Recycling initiatives where segregated waste is picked up, recycled, and repurposed for use in construction or manufacturing.
3. Water Conservation and Management:
- Smart water meters that help in detecting leaks, ensuring efficient water distribution, and promoting water conservation.
- Rainwater harvesting systems integrated into the urban infrastructure to supplement water supply and reduce reliance on municipal water.
- Water-efficient appliances and public awareness campaigns to reduce water wastage.
4. Clean and Green Environment:
- Green spaces such as parks, vertical gardens, and green rooftops to improve air quality and provide recreational areas for residents.
- Urban farming initiatives like rooftop gardens and community farming to promote local food production and reduce transportation emissions.
- Electric waste management through the collection and disposal of electronic waste (e-waste) in an environmentally friendly manner.
5. Smart Healthcare and Education:
- Telemedicine facilities and health apps that enable residents to access medical consultations and health tracking remotely.
- Smart classrooms and e-learning platforms to enhance access to quality education and facilitate lifelong learning.
6. Affordable Housing:
- Low-cost smart housing designs that incorporate energy-efficient appliances and sustainable building materials to reduce living costs.
- Public-private partnerships to build affordable housing with modern amenities, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for all income groups.
7. Data-Driven Governance:
- City-wide Wi-Fi and mobile applications that allow citizens to report issues, access city services, and provide feedback.
- Data analytics for efficient urban planning and resource allocation, ensuring that every resident benefits from the city’s growth.
- Smart policing through CCTV cameras, predictive policing technologies, and real-time crime data analysis to improve public safety.
Conclusion:
This smart city proposal emphasizes a harmonious integration of advanced technology with sustainable practices to create an environment that is not only technologically advanced but also ecologically balanced and affordable for all residents.
23. Enumerate the challenges confronting society regarding the adolescent population. Enlist a few measures to overcome these problems.
Challenges Confronting Society Regarding the Adolescent Population:
- Mental Health Issues: Adolescents often experience stress, depression, anxiety, and identity crises, compounded by peer pressure and academic pressure.
- Substance Abuse: Adolescents are vulnerable to experimenting with substances like drugs, alcohol, and tobacco, leading to addiction and health risks.
- Educational Pressure: Intense competition and pressure to perform well in exams may result in burnout and mental distress.
- Early Sexuality and Unwanted Pregnancies: Adolescents may not have adequate awareness or protection, leading to early pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases.
- Cyberbullying and Online Addiction: With the rise of digital platforms, adolescents are exposed to cyberbullying, online harassment, and excessive screen time.
- Violence and Abuse: Some adolescents face physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, which can severely affect their development.
Measures to Overcome These Problems:
- Mental Health Support: Establish counseling services in schools and communities to help adolescents cope with mental health issues. Awareness campaigns to reduce the stigma around mental health.
- Substance Abuse Prevention Programs: Introduce educational programs in schools to raise awareness about the dangers of drugs and alcohol, along with providing alternative recreational activities.
- Balanced Education System: Create a more holistic education system that focuses on both academic and emotional well-being, reducing the overemphasis on exams.
- Sex Education and Health Awareness: Implement comprehensive sex education in schools to promote safe sexual practices and prevent unwanted pregnancies and STDs.
- Digital Literacy and Safety: Educate adolescents about responsible online behavior, including identifying cyberbullying and setting limits on screen time.
- Protection from Abuse: Strengthen laws and systems to protect adolescents from physical, emotional, and sexual abuse. Provide a safe space for reporting abuse.
24. How does food gathering as an economic activity differ between primitive and modern societies, and why is it unlikely to significantly influence the global economy today?
Answer:
Food Gathering in Primitive Societies:
In primitive societies, food gathering was primarily a subsistence activity. People depended on hunting, fishing, and gathering wild plants to meet their basic needs. This type of food gathering was closely linked to the local environment, with individuals or small groups foraging for food within a limited geographical area. The practice was labor-intensive and seasonal, influenced by the availability of resources and climate conditions. It was directly connected to the survival of the group and had minimal economic impact beyond local self-sufficiency.
Food Gathering in Modern Societies:
In contrast, modern societies have transitioned from food gathering to food production, particularly through agriculture and industrial food processing. The global food industry today involves large-scale agricultural practices, mechanization, and sophisticated supply chains that produce food at an industrial level. Modern societies rely on global trade, technological advancements in farming, and chemical inputs (fertilizers, pesticides) to enhance production. Food gathering as an activity is almost obsolete in urbanized societies, and agriculture plays a significant role in economic growth, trade, and industrial development.
Why is it Unlikely to Influence the Global Economy Today?
Food gathering, as practiced by primitive societies, is unlikely to influence the global economy today for several reasons:
- Transformation to Agriculture and Industry: The evolution of farming, agriculture, and food production technologies has greatly reduced the importance of gathering wild food in the modern economy.
- Global Food Supply Chains: Food production today is a highly commercialized industry with global supply chains, where regions specialize in specific crops or livestock. Food gathering doesn’t contribute to these complex global networks.
- Technological Advancements: Modern farming techniques, such as the use of machinery and genetically modified crops, have far outpaced traditional food gathering methods.
25. A. Assess the factors that contributed to the development of large-scale industries all over the world.
Answer:
The development of large-scale industries worldwide can be attributed to several factors:
-
Technological Advancements:
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries introduced new technologies such as the steam engine, mechanized looms, and advanced machinery, which allowed industries to increase production and efficiency. Automation and the development of electronics and robotics further revolutionized manufacturing processes. -
Access to Raw Materials:
Industries grew in regions rich in natural resources like coal, iron ore, petroleum, and agricultural products. Availability of raw materials was crucial for industries such as steel production, textiles, and chemicals. -
Capital Investment:
The influx of capital investment from governments, private entrepreneurs, and financial institutions enabled the establishment and expansion of factories and industries. Industrial growth was often supported by loans, grants, and foreign investments. -
Transportation and Communication:
Efficient transportation systems, such as railways, roads, and ports, facilitated the movement of raw materials and finished goods. Advances in communication (telegraphs, phones, internet) allowed for better coordination, marketing, and global trade. -
Urbanization and Labor Supply:
The rise of urban centers provided a large labor force, as people moved from rural areas to cities in search of work. Additionally, factory work and the emergence of wage labor provided new employment opportunities. -
Government Policies and Global Trade:
Governments often supported industrial growth through favorable policies like tax incentives, subsidies, and infrastructure development. Global trade networks facilitated the export of industrial goods to international markets.
25. B. Access to transportation and communication facilities are essential for the development of industries. Justify the statement with a suitable example.
Answer:
Access to transportation and communication facilities is critical for the development of industries, as these factors directly affect the flow of raw materials, finished products, and information. Efficient transportation ensures that raw materials can be sourced from distant locations and delivered to factories, while communication facilitates the coordination and management of industrial processes.
Example:
The automobile industry in Germany (e.g., companies like Volkswagen and BMW) is a perfect example of how transportation and communication infrastructure contribute to industrial development. The country’s well-developed transportation network, including roads, railways, and ports, facilitates the movement of raw materials such as steel and plastics to production facilities. The use of advanced communication technologies enables coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and international markets. This efficient system has helped Germany become a global leader in the automobile industry.
26. A. Evaluate the benefits derived from the Integrated Tribal Development Project implemented in the Bharmaur Region.
Answer:
The Integrated Tribal Development Project (ITDP) in the Bharmaur region of Himachal Pradesh was implemented to address the socio-economic challenges faced by tribal communities. This project aimed to provide better living standards, health facilities, education, and economic opportunities to the tribal people.
Benefits:
-
Improved Infrastructure:
The ITDP led to the construction of roads, schools, and healthcare facilities in remote tribal areas, improving access to basic services. This enhanced mobility and facilitated better living conditions for the tribal population. -
Economic Empowerment:
The project focused on promoting local handicrafts and agro-based industries, helping tribal communities generate income through the sale of their products. This has reduced dependence on government aid and created sustainable livelihoods. -
Health and Sanitation:
The introduction of health camps, sanitation facilities, and awareness programs about hygiene improved the health outcomes of the tribal population. The incidence of diseases declined due to better medical facilities and sanitation. -
Educational Opportunities:
The establishment of schools and vocational training centers helped enhance literacy rates and provided skills training, contributing to the overall development of the tribal communities. -
Preservation of Culture:
The ITDP supported the preservation of the unique cultural heritage of the tribals while integrating modern practices. This helped in improving their socio-economic conditions without losing their cultural identity.
26. B. ‘Hill Area Development Programmes were initiated for the specified areas keeping in view their topographical, ecological, social, and economic conditions’. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Hill Area Development Programmes (HADPs) were specifically designed to address the unique challenges faced by hilly and mountainous regions in India. These areas have distinct topographical, ecological, social, and economic conditions that necessitate specialized development strategies.
Justification:
-
Topographical Challenges:
Hill areas are often characterized by rugged terrain, steep slopes, and difficult accessibility. These geographical features make transportation and infrastructure development challenging. HADPs focus on improving road connectivity, promoting terrace farming, and creating infrastructure suitable for hilly terrain. -
Ecological Concerns:
The ecological balance in hilly regions is fragile due to deforestation, soil erosion, and the risk of landslides. HADPs aim to preserve the environment by promoting afforestation, watershed management, and soil conservation techniques. -
Social Factors:
The hill areas often have distinct social practices, cultures, and lifestyles. HADPs take these into account by promoting local participation in development programs, ensuring that development is culturally sensitive and inclusive. This helps in creating awareness about health, education, and sanitation in remote tribal and rural communities. -
Economic Conditions:
The economy of hill areas is primarily agrarian, with limited industrial or commercial activity. HADPs promote sustainable agriculture, agro-based industries, and eco-tourism to generate income and employment, thereby improving the economic conditions of the people.
27. A. The composition of commodities in India’s international trade has been undergoing a change over the years. Substantiate the statement with suitable arguments.
Answer:
The composition of India’s international trade has indeed undergone significant changes in recent decades. Traditionally, India’s trade was dominated by agricultural products and raw materials. However, with the development of its industrial and service sectors, the composition of exports and imports has evolved.
-
Shift from Primary Products to Manufactured Goods:
Earlier, India exported primarily agricultural products (tea, coffee, spices) and raw materials (cotton, minerals). Today, the share of manufactured goods (such as textiles, engineering products, chemicals, and electronics) in India’s exports has increased significantly. -
Growth of Services Exports:
India’s export basket has diversified to include a significant portion of services, especially in information technology (IT), business process outsourcing (BPO), and software services. The rise of the IT sector has transformed India into a global leader in technology services. -
Changing Import Composition:
While India continues to import oil and gold, there has been a notable increase in imports of technology, machinery, and chemicals due to the expansion of the industrial and manufacturing sectors. -
Regional Shifts in Trade:
India’s trade partners have diversified as well. The country now has significant trade relationships with countries in East Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, in addition to traditional partners like the United States and Europe.
27. B. ‘Air transport plays an important role in international trade’. Justify the statement with suitable arguments.
Answer:
Air transport plays a vital role in international trade, especially for goods that require quick delivery, high value, or perishable nature. Here’s why air transport is critical for global trade:
-
Fast Delivery:
Air transport is the fastest mode of transportation, enabling businesses to deliver products quickly across long distances. This is particularly crucial for industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and fashion, where speed is key to maintaining a competitive edge in global markets. -
High-Value Goods:
Air transport is preferred for transporting high-value, low-weight items like electronic goods, jewelry, and luxury items. These goods may not be economical to transport via sea or land due to their high insurance and security costs. -
Perishable Goods:
Perishable goods such as fresh produce, flowers, and seafood require rapid transportation to avoid spoilage. Air transport allows these goods to be delivered fresh, ensuring that they reach international markets in prime condition. -
Connectivity:
Air transport enhances connectivity between distant markets and provides access to remote regions. It also helps in expanding the global reach of businesses, allowing them to explore international markets efficiently. -
Trade in Technology and Services:
Air transport facilitates the movement of technology, machinery, and parts, supporting international trade in high-tech industries and manufacturing sectors.
28. A. ‘Environmental pollution by solid wastes has now got significance due to the enormous growth in the quantity of waste’.
Answer:
The enormous growth in the quantity of solid waste has become a significant environmental concern for several reasons:
-
Increase in Urbanization:
As cities expand and populations grow, the amount of waste generated in urban areas has increased dramatically. High consumption levels in urban areas lead to larger quantities of industrial waste, household waste, and commercial waste. -
Non-Biodegradable Materials:
The rise in the use of non-biodegradable materials such as plastics has aggravated the problem. These materials do not break down naturally and remain in the environment for long periods, causing pollution in landfills, rivers, and oceans. -
Waste Disposal Challenges:
Many developing countries lack efficient waste management systems, leading to improper disposal of solid waste, which contributes to pollution of soil, water, and air. Open dumping and burning of waste release harmful toxins into the environment. -
Health Hazards:
Improper handling of waste can lead to serious health problems, as it attracts pests and spreads diseases. Contaminated water sources and air pollution from burning waste also have significant health impacts on the population.
28. B. Give reasons for the unsustainable increase in solid waste and discuss two strategies to control waste generation at the source in urban areas.
Answer:
Reasons for Unsustainable Increase in Solid Waste:
-
Increased Consumption:
With rising affluence, urban populations tend to consume more products, leading to an increase in packaging materials and non-essential goods that contribute to waste. -
Disposable Culture:
The growing preference for single-use, disposable products, such as plastic bottles, bags, and food packaging, has led to an explosion of non-biodegradable waste. -
Lack of Waste Segregation:
In many urban areas, waste is not segregated at the source, leading to contamination of recyclable materials and the increase of mixed waste, which is harder to manage.
Strategies to Control Waste Generation:
-
Promote Waste Segregation:
Encouraging households and businesses to segregate waste into recyclable, biodegradable, and non-recyclable categories can significantly reduce the overall waste load. This enables effective recycling and composting, reducing the burden on landfills. -
Encourage Reduced Packaging and Sustainable Products:
Governments and industries should work together to reduce unnecessary packaging, promote reusable packaging, and develop products made from sustainable materials. Consumer awareness campaigns can also play a key role in encouraging eco-friendly consumption habits.

Question 29:
On the given political map of the World, seven geographical features have been marked as A, B, C, D, E, F and G. Identify any five with the help of the following
A. A major seaport.
Answer: Rotterdam (Netherlands)
B. An international airport.
Answer: Heathrow Airport (London, UK)
C. An important Seaway.
Answer: Suez Canal
D. An area of subsistence gathering in South America.
Answer: Amazon Rainforest
E. An important seaport of Asia.
Answer: Shanghai (China)
F. An area of Nomadic Herding.
Answer: Mongolia
G. Region of extensive commercial grain agriculture.
Answer: Great Plains of North America
Certainly, let’s answer the questions for Visually Impaired Candidates:
29 A. Name a major seaport situated at the southernmost tip of Africa.
Answer: Cape Town
29 B. Name an important international airport of Italy.
Answer: Leonardo da Vinci–Fiumicino Airport (Rome)
29 C. Which river in North America connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean?
Answer: St. Lawrence River
29 D. Name an area of subsistence gathering in South America.
Answer: Amazon Rainforest
29 E. Name an important sea port of China.
Answer: Shanghai
29 F. Mention an area of nomadic herding in North Africa.
Answer: Sahara Desert
29 G. Name the area of extensive commercial grain agriculture in New Zealand.
Answer: Canterbury Plains
30 Locate and label any five of the following geographical features on the Political
Outline map of India with appropriate symbols:
A. An important coal mine in Orisha.
B. An important seaport in Karnataka.
C. Jharia – Coal mines.
D. An oil refinery in Uttar Pradesh.
E. The state with lowest population density.
F. The state leading in the production of Tea.
G.An international airport in Punjab.
The following questions are for visually impaired students in lieu of
Question No.30. Attempt any five.
30.A Name an important coal mine in Orisha.
30.B Name an important seaport in Karnataka.
30.C Name one important coal mine of Maharashtra
30.D Name one oil refinery of Uttar Pradesh.
30.E Name the state with lowest population density.
30.F Name one leading tea producing state of India.
30.G Name the international airport of Punjab.