Section A (MCQs)
- When was Meiji Constitution of 1889 replaced by a new constitution?
a) 1905
b) 1911
c) 1943
d) 1947
Answer: d) 1947 - Mesopotamia is in modern ________.
a) Iran
b) Syria
c) Egypt
d) Iraq
Answer: d) Iraq - ________ family was considered as the norm in Mesopotamian society.
a) Nuclear
b) Joint
c) Compound
d) All of these
Answer: b) Joint - Identify the given image from the following options:
a) Amphitheatre at Vindonissa
b) Wine merchant’s dining room in Pompeii
c) Pont du Gard, near Nimes, France
d) Shops in Forum Julium, Rome
Answer: b) Wine merchant’s dining room in Pompeii - Assertion (A): Next to the emperor and the Senate, the other key institution of imperial rule was the army and the army hated and feared the senate.
Reason (R): Army was a source of often unpredictable violence, especially in the tense conditions of the third century when the government was forced to tax more heavily to pay for its mounting military expenditures.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true.
Answer: a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. - What was the period of Guyuk’s reign?
a) 1246 to 1248
b) 1247-1249
c) 1246 to 1270
d) 1236-1246
Answer: b) 1247-1249 - Assertion (A): The name Mesopotamia is derived from the Greek words mesos and potamos.
Reason (R): Mesopotamia is the land between three main rivers- Great Zab, Euphrates and the Tigris rivers.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true.
Answer: c) A is true but R is false. - Identify an anthropologist with the help of the following information:
He composed a lecture on The Great Australian Silence.
He condemned historians for not making any records of aborigines.
a) W.E.H. Stanner
b) Henry Reynolds
c) James Cook
d) Judith Wright
Answer: a) W.E.H. Stanner - Where did Feudalism take her roots?
a) England
b) France
c) Germany
d) Italy
Answer: b) France - Consider the following statements and select the correct from the following option:
- Ur was a town whose ordinary houses were systematically excavated in the 1930s.
- Narrow winding streets in Ur indicate that wheeled carts could not have reached many of the houses.
- Narrow winding streets and the irregular shapes of house plots in Ur indicate a perfect town planning.
a) i and iii
b) ii and iii
c) i, ii and iii
d) i and ii
Answer: d) i and ii
- Find out the correct chronological order from the following options:
- Brunelleschi designs the Duomo in Florence
- Geoffrey Chaucer’s Canterbury Tales published
- University established in Florence
- Ottoman Turks defeat the Byzantine ruler of Constantinople
a) iv, ii, i, iii
b) i, ii, iii, iv
c) iii, ii, i, iv
d) ii, iii, iv, i
Answer: b) i, ii, iii, iv
- When was the Treaty of Shimonoseki signed?
a) 1897
b) 1890
c) 1893
d) 1895
Answer: d) 1895 - Which among the following is Correctly matched?
- (A) Thomas More’s – Ninety-Five Theses
- (B) Martin Luther – Utopia
- (C) Isaac Newton – Principia Mathematica
- (D) Andreas Vesalius – The Social Contract
a) Option (D)
b) Option (B)
c) Option (C)
d) Option (A)
Answer: c) Option (C) Isaac Newton – Principia Mathematica
- Who collected taille?
a) The Priest
b) The Nobles
c) The Peasantry
d) The King (Monarch)
Answer: c) The Peasantry - Edo is now called ________.
a) Tokyo
b) Singapore
c) Hong Kong
d) Shanghai
Answer: a) Tokyo - Roman Empire was seized by ________.
a) Arabian
b) Egyptian Empire
c) Mesopotamians
d) Sassanians
Answer: d) Sassanians - Who defeated the Sung ruler of southern China?
a) Churk Buka
b) Qubilai Khan
c) Arik Buka
d) Toluy
Answer: b) Qubilai Khan - Assertion (A): In the reign of Louis XIII of France, a meeting was held of the French consultative assembly. After this, it was not summoned again for nearly two centuries, till 1789.
Reason (R): The first order i.e. clergy did not want to share power with the three orders.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true.
Answer: a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. - Which of these statements is false about Cicero?
a) He was a Roman essayist
b) He was a Roman lawyer
c) He was contemporary to Julius Caesar
d) He was a British officer
Answer: d) He was a British officer - Match the following and select the correct option:
- 1603 – A. Tokugawa Ieyasu establishes the Edo shogunate
- 1868 – B. Korea annexed
- 1889 – C. Meiji Constitution enacted
- 1910 – D. Restoration of Meiji
a) 1 – a, 2 – d, 3 – c, 4 – b
b) 1 – b, 2 – c, 3 – d, 4 – a
c) 1 – c, 2 – b, 3 – d, 4 – a
d) 1 – d, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – c
Answer: a) 1 – a, 2 – d, 3 – c, 4 – b
- It laid the foundation for the prosperity of Australia:
a) Agriculture
b) Fishing Industry
c) Mining Industry
d) Construction Industry
Answer: c) Mining Industry
section – B
1. Discuss the key characteristics of feudalism in medieval Europe. How did it impact the social, political, and economic systems of the time?
Answer:
Feudalism in medieval Europe was a hierarchical system of land ownership and duties that defined the relationships between lords, vassals, and serfs.
- Social Structure: Society was divided into rigid classes, including the king, nobles (lords), knights, and peasants.
- Political Structure: Power was decentralized, with local lords controlling land and administering justice. The king had limited direct control over the territories.
- Economic System: The economy was agrarian, with serfs working on the land in exchange for protection and a small portion of the produce.
- Impact: Feudalism contributed to a lack of centralization and a strong dependence on agriculture. It also hindered trade and industrial development during the Middle Ages.
2. What were the primary causes and outcomes of the Protestant Reformation? How did it change the religious landscape of Europe?
Answer:
- Causes:
- Corruption within the Catholic Church: Practices such as indulgences and the wealth of the clergy caused widespread dissatisfaction.
- Martin Luther’s 95 Theses (1517): Luther’s criticism of church practices sparked the Reformation.
- Printing Press: The invention of the printing press helped spread Reformation ideas rapidly across Europe.
- Outcomes:
- Religious Fragmentation: The Reformation led to the establishment of Protestant churches, dividing Europe between Catholicism and Protestantism.
- Decline of Church Power: The Catholic Church lost political influence, and monarchs gained more power.
- Religious Wars: Conflicts such as the Thirty Years’ War occurred as a result of the Reformation.
3. Describe the significance of the Roman Empire’s expansion into Mesopotamia. How might the culture, governance, and trade systems have been affected if Rome had successfully conquered India?
Answer:
- Roman Expansion into Mesopotamia: The Roman Empire expanded into Mesopotamia but faced challenges from the Parthian Empire. Control over Mesopotamia brought Rome into contact with Eastern trade routes and cultures.
- Impact on India if Rome Conquered It:
- Cultural Exchange: The Romans may have influenced Indian art, architecture, and religion, introducing Roman cultural elements like roads, baths, and monumental buildings.
- Trade: Rome would have gained access to India’s luxury goods, such as spices, textiles, and precious stones. This could have strengthened the Roman economy.
- Political System: Roman-style governance, with a centralized system and legal structures, might have influenced India’s political administration.
4. Explain the factors that contributed to the Guomindang’s failure in uniting China in the early 20th century.
Answer:
- Internal Division: The Guomindang (Nationalist Party) was divided between its leaders, with differing ideologies and strategies.
- Weak Support Base: The Guomindang had limited support from the rural population and lacked a strong military presence.
- Conflict with the Communist Party: The Guomindang’s tension with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) led to civil war.
- Japanese Invasion: The Japanese invasion in the 1930s further destabilized China, and the Guomindang’s failure to effectively counter the invasion weakened its position.
- Corruption: Corruption within the Guomindang government eroded its support and made it less effective in governance.
5. What is meant by the ‘division of labor’ in the context of urban life? Provide examples of how division of labor shapes different sectors of society.
Answer:
The division of labor refers to the way in which tasks are divided among different individuals or groups in a society, leading to specialization in specific jobs.
- Example in Urban Life: In cities, people specialize in various sectors such as healthcare (doctors, nurses), transportation (drivers, conductors), and education (teachers, administrators).
- Impact on Society:
- Increased Productivity: Specialization allows for more efficient production and services.
- Social Stratification: The division of labor often leads to the creation of different social classes based on occupation, such as skilled workers, service workers, and professionals.
6. Discuss the contributions of the southern region of Mesopotamia to the development of early civilization.
Answer:
- Urbanization: Southern Mesopotamia, particularly the Sumerian region, saw the rise of some of the world’s first cities, such as Ur and Uruk.
- Writing System: The Sumerians developed cuneiform writing, one of the earliest known forms of written language, which was used for record-keeping, legal documentation, and literature.
- Inventions: The Mesopotamians invented the wheel, developed complex irrigation systems, and created a base-60 number system.
- Religion: The region had large temples and ziggurats dedicated to gods, reflecting the importance of religion in everyday life.
- Trade: Mesopotamia’s location between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers made it a hub for trade, connecting different civilizations.
SECTION – C
7. How did Genghis Khan’s military campaigns contribute to the expansion of the Mongol Empire?
Answer:
- Military Strategy: Genghis Khan employed innovative tactics, including surprise attacks, psychological warfare, and the use of well-organized, highly mobile cavalry.
- Unification of Mongol Tribes: Before his campaigns, Mongol tribes were fragmented. Genghis Khan united them, forming a strong and cohesive military force.
- Conquests: His military campaigns were vast, resulting in the conquest of Central Asia, China, and parts of the Middle East. He broke through the Great Wall of China and defeated the Khwarazm Empire.
- Legacy: Genghis Khan’s empire became the largest contiguous empire in history, stretching from Europe to Asia, fostering cultural exchange and trade through the Silk Road.
8. Discuss the causes behind the decline of the Shogunate system in Japan.
Answer:
- Internal Weaknesses: The Tokugawa Shogunate faced internal divisions and corruption within the ruling class, weakening its control.
- Economic Issues: Japan faced financial crises due to rising military costs and inefficient agricultural practices.
- External Pressure: The arrival of Commodore Perry in 1853 and the forced opening of Japan to foreign trade led to resentment and social unrest.
- Reform Movements: The samurai class, which had been the backbone of the Shogunate, began pushing for reforms. Eventually, the imperial restoration led to the downfall of the Shogunate in 1868.
9. Explain the significance of cuneiform writing in ancient Mesopotamia. How did it evolve and what impact did it have on the development of Mesopotamian society?
Answer:
- Cuneiform Development: Cuneiform writing began around 3200 BCE as a system of pictographs to record trade transactions. Over time, it evolved to represent sounds and ideas.
- Impact on Mesopotamian Society:
- Record-Keeping: Cuneiform was used for administrative purposes, helping organize trade, laws, and taxes.
- Literature and Religion: It allowed the recording of religious texts, myths (such as the Epic of Gilgamesh), and literature, preserving Mesopotamian culture.
- Education and Administration: Cuneiform literacy was an essential skill for scribes, who played an important role in the administration of the city-states.
- Legacy: Cuneiform influenced later writing systems and played a key role in the development of record-keeping and communication.
10. How did the Gold Rush contribute to the economic and political expansion of the United States in the 19th century?
Answer:
- Economic Impact: The Gold Rush, particularly the California Gold Rush of 1849, attracted thousands of settlers and led to the rapid development of mining towns. The influx of wealth contributed to the growth of infrastructure such as railroads, banks, and cities.
- Political Impact: The Gold Rush accelerated the process of statehood for regions like California, which became a state in 1850.
- Social Consequences: It contributed to the displacement of Native American populations and the expansion of slavery, creating tensions that led to the Civil War.
- Migration: The promise of gold led to a significant migration from other parts of the U.S. and abroad, particularly from China, Europe, and Latin America.
Section D: Source-Based Questions
Passage 1:
Formal education was not the only way through which humanists shaped the mind of their age. Art, architecture and books were wonderfully effective in transmitting humanist ideas. Artists were inspired by studying works of the past. The material remains of Roman culture were sought with as much excitement as ancient text: a thousand years after the fall of Rome, fragments of art were discovered in the ruins of ancient Rome and other deserted cities. Their admiration for the figures of perfectly proportioned men and women sculpted so many centuries ago, made Italian sculptors want to continue that tradition. In 1416, Donatello (1386-1456) broke new ground with his life-like statues. Artists’ concern to be accurate was helped by the work of scientists.
- Besides education, in what other ways did the humanists shape the minds of their age?
Answer:
Humanists shaped the minds of their age not only through formal education but also through art, architecture, and books, which were highly effective in transmitting humanist ideas. - Examine the sentence: “Artists’ concern to be accurate was helped by the work of scientists.”
Answer:
This sentence suggests that artists, while striving for accuracy in their work, were aided by scientific advancements. Scientific methods, particularly in areas such as anatomy and proportion, helped artists understand and replicate human figures more precisely, contributing to more realistic and lifelike art. - What was the source of inspiration for the artists?
Answer:
The material remains of Roman culture, such as ancient sculptures and texts, served as the primary source of inspiration for the artists. They admired and sought to replicate the perfectly proportioned figures of men and women sculpted during the Roman era.
Passage 2:
Slavery was an institution deeply rooted in the ancient world, both in the Mediterranean and in the Near East, and not even Christianity when it emerged and triumphed as the state religion (in the fourth century) seriously challenged this institution. It does not follow that the bulk of the labour in the Roman economy was performed by slaves. That may have been true of large parts of Italy in the Republican period (under Augustus there were still 3 million slaves in a total Italian population of 7.5 million) but it was no longer true of the empire as a whole. Slaves were an investment, and at least one Roman agricultural writer advised landowners against using them in contexts where too many might be required (for example, for harvests) or where their health could be damaged (for example, by malaria). These considerations were not based on any sympathy for the slaves but on hard economic calculation. On the other hand, if the Roman upper classes were often brutal towards their slaves, ordinary people did sometimes show much more compassion. See what one historian says about a famous incident that occurred in the reign of Nero. As warfare became less widespread with the establishment of peace in the first century, the supply of slaves tended to decline and the users of slave labour thus had to turn either to slave breeding or to cheaper substitutes such as wage labour which was more easily dispensable. In fact, free labour was extensively used on public works at Rome precisely because an extensive use of slave labour would have been too expensive. Unlike hired workers, slaves had to be fed and maintained throughout the year, which increased the cost of holding this kind of labour. This is probably why slaves are not widely found in the agriculture of the later period, at least not in the eastern provinces. On the other hand, they and freedmen, that is, slaves who had been set free by their masters, were extensively used as business managers, where, obviously, they were not required in large numbers. Masters often gave their slaves or freedmen capital to run businesses on their behalf or even businesses of their own.
- Infer the reason for the decline in the supply of slaves in the first century.
Answer:
The decline in the supply of slaves in the first century was due to the reduced frequency of warfare, which had been a primary source of slaves. As peace spread across the empire, there were fewer wars to capture slaves, leading to a decline in the number of slaves available for labor. - Prudent landowners gradually switched over to slave breeding or hiring paid laborers. What is slave breeding?
Answer:
Slave breeding refers to the practice of breeding slaves in order to increase the supply of labor. This method was used by landowners to ensure a steady and reliable workforce, as the availability of new slaves from warfare decreased. - Why were the landowners advised against using slaves where too many of them were required?
Answer:
Landowners were advised against using too many slaves for tasks such as harvests because it would increase the cost of maintaining them. Slaves had to be fed and taken care of year-round, which made them more expensive to hold in large numbers compared to hiring free labor, which was more flexible and disposable.
Passage 3:
**Because of the inadequacy which we often felt on feast days, for the narrowness of the place forced the women to run towards the altar upon the heads of the men with much anguish and noisy confusion, [we decided] to enlarge and amplify the noble church…
We also caused to be painted, by the exquisite hands of many masters from different regions, a splendid variety of new windows… Because these windows are very valuable on account of their wonderful execution and the profuse expenditure of painted glass and also a goldsmith… who would receive their allowances, namely, coins from the altar and flour from the common storehouse of the brethren, and who would never neglect their duty, to look after these [works of art].
- Abbot Suger (1081-1151) about the Abbey of St Denis, near Paris.
- Why was it decided to enlarge and amplify the noble Church?
Answer:
The decision to enlarge and amplify the church was made because the narrowness of the place was causing inconvenience, particularly on feast days. Women were forced to run over the heads of the men to reach the altar, creating angst and confusion. Therefore, expanding the church was seen as a solution to improve the space for worshippers. - With what names were the big churches called?
Answer:
The large churches, such as the Abbey of St. Denis, were often referred to as “noble churches” due to their grandeur and importance in the religious and social life of the time. - Why were an official master craftsman and a goldsmith appointed in the big churches?
Answer:
An official master craftsman and a goldsmith were appointed in the big churches to ensure the proper maintenance and creation of high-quality works of art, such as stained-glass windows. The master craftsman was responsible for overseeing the artistic creations, while the goldsmith managed the precious materials used, ensuring the value and proper execution of the artwork. They were given allowances and duties related to their tasks in the church, such as receiving coins from the altar and flour from the storehouse of the brethren.
Section E
-
- On the given map of Britain, locate and label the industrial areas with appropriate symbols:
- Glasgow
- Newcastle
- Nottingham
OR - Leicester
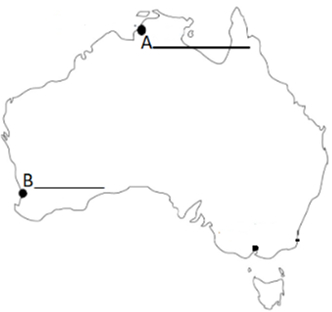
- On the given map, three places have been marked as A and B which are associated with human habitation in Australia in the early period. Identify any two of them and write their correct names on the lines marked near them.
- On the given map of Britain, locate and label the industrial areas with appropriate symbols:
